Overview
Milling is a fundamental machining process that uses a rotary cutter to remove material from a workpiece. This versatile technique is employed in various industries, from aerospace and automotive to manufacturing and construction. At the heart of milling lies the milling cutter, a tool with diverse types, each designed for specific tasks. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the world of milling cutters, exploring their types, features, and functions, and gaining a better understanding of their pivotal role in machining processes.

Introduction to Milling Cutters
Milling cutters are rotary tools used in milling machines to perform various machining operations, such as cutting, shaping, and contouring. They are available in a wide range of shapes, sizes, and materials, each tailored to specific tasks. Milling cutters play a critical role in achieving precision and accuracy in machining processes. Let’s begin by examining the primary types of milling cutters.

Types of Milling Cutters
1. End Mill
End mills are versatile tools suitable for various milling operations, including facing, contouring, slot cutting, and drilling. They come in a variety of configurations, such as square end, ball end, and corner radius end mills, each optimized for specific tasks.
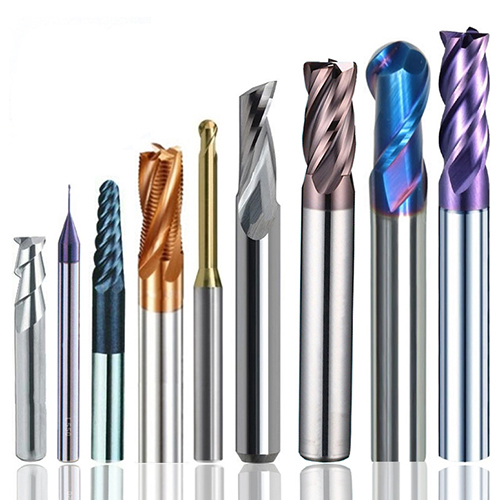
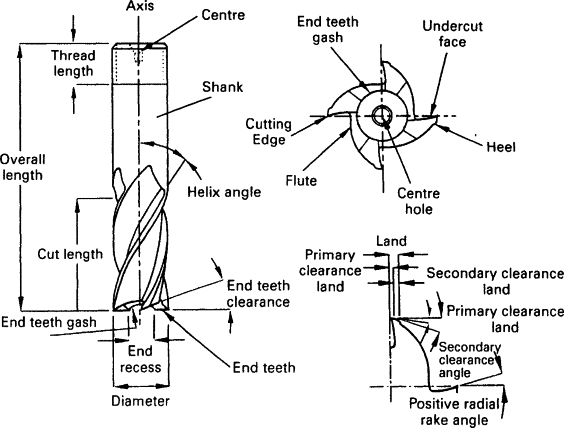

- Features:
- Cutting edges at the tip and sides.
- Available in different lengths, diameters, and coatings.
- Suitable for profiling and pocketing operations.
- Various fluting options for chip evacuation.
- Functions:
- Profiling and contouring workpieces.
- Creating slots and pockets.
- Drilling holes.
2. Face Mill
Face mills are designed for facing large, flat surfaces of a workpiece. They feature multiple cutting edges on the periphery of a rotating disc. Face mills come in various diameters and insert configurations, allowing for efficient material removal and surface finishing.

- Features:
- Multiple cutting edges on the face.
- Inserts or replaceable cutters for cost-effective maintenance.
- Suitable for high-speed machining of flat surfaces.
- Often used in milling machines with vertical spindles.
- Functions:
- Facing large, flat workpieces.
- Surface milling for precision finishing.
3. Ball Nose Cutter
Ball nose cutters have a rounded cutting end, resembling a ball. They are primarily used for 3D profiling and contouring tasks, as the rounded tip allows for smooth and precise machining on curved surfaces.
- Features:
- Spherical or rounded cutting tip.
- Available in various sizes and materials.
- Ideal for complex 3D machining.
- Reduces the risk of tool marks and chatter.
- Functions:
- 3D profiling.
- Contouring complex surfaces.
- Creating sculpted shapes.
4. T-slot Cutter
T-slot cutters are specialized tools used for creating T-shaped slots or grooves in workpieces. These cutters have a distinctive T-shaped profile and come in various sizes to accommodate different T-slot dimensions.

- Features:
- T-shaped cutting profile.
- Available in various widths and depths.
- Used for creating T-slots for bolts, nuts, and other fasteners.
- Commonly used in machine tool setups and fixturing.
- Functions:
- Cutting T-slots for securing workpieces.
- Facilitating precise positioning and clamping.
5. Shell Mill Cutter
Shell mill cutters are large-diameter cutters with multiple insert pockets on their periphery. They are designed for heavy-duty machining operations, such as face milling and slab milling, where material removal rates are high.
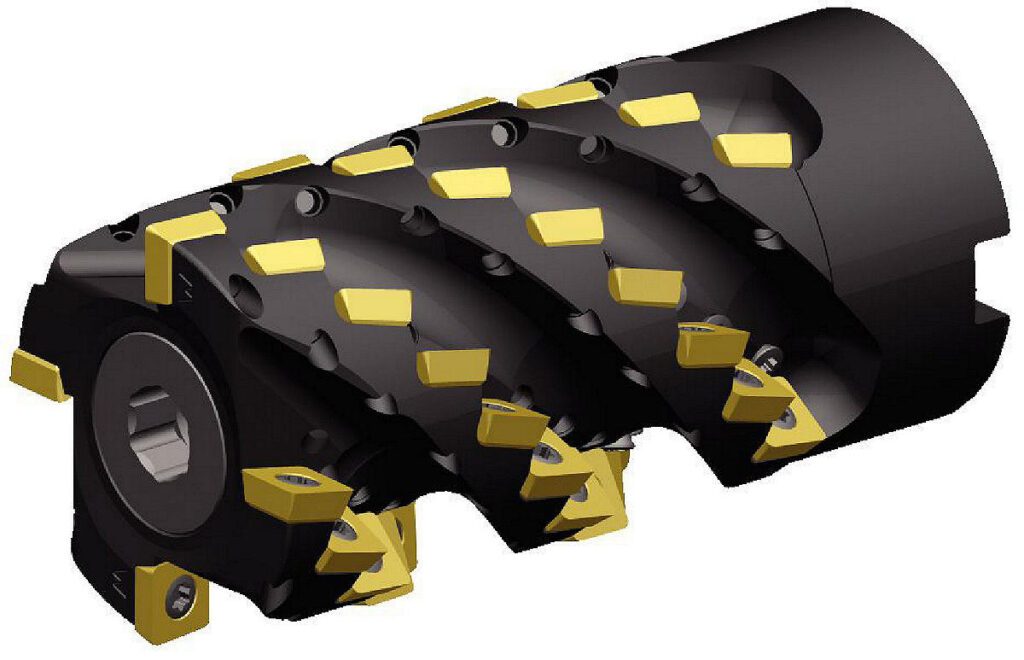

- Features:
- Large diameter with multiple insert pockets.
- Suitable for high-speed machining.
- Excellent chip evacuation capabilities.
- Ideal for roughing and finishing operations.
- Functions:
- Face milling of large workpieces.
- High-volume material removal.
6. Slitting Saw
Slitting saws are thin, disc-shaped cutters with teeth on the periphery. They are used for making narrow cuts or slots in workpieces. Slitting saws come in various diameters and widths to suit different slotting requirements.
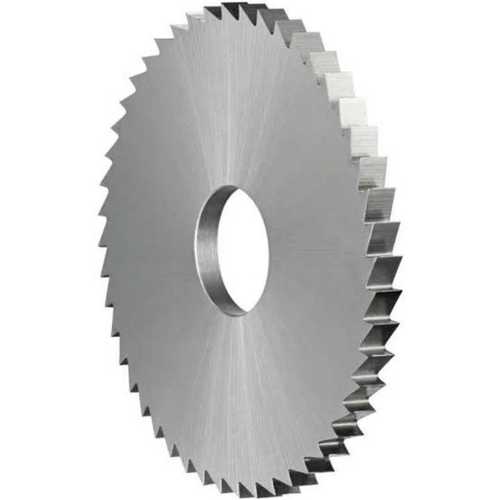

- Features:
- Thin, disc-like shape.
- Multiple teeth around the periphery.
- Available in various tooth geometries.
- Suitable for precision slotting and cut-off operations.
- Functions:
- Cutting narrow slots or grooves.
- Parting-off operations.
7. Fly Cutter
A fly cutter is a single-point cutting tool attached to the spindle of a milling machine. It is a simple yet effective cutter for facing and surfacing operations. Fly cutters are known for their versatility and ease of use.
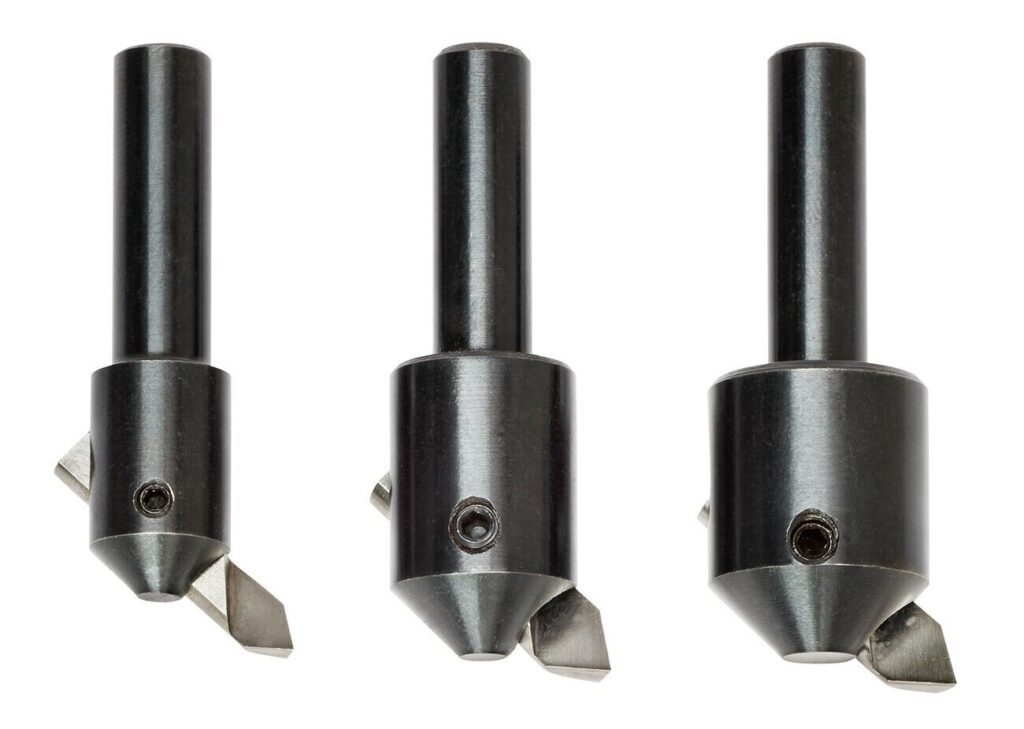

- Features:
- Single-point cutting tool.
- Mounts directly on the milling machine spindle.
- Typically used for manual machining.
- Functions:
- Facing flat surfaces.
- Surface finishing.
8. Thread Mill
Thread mills are specialized cutters used for machining threads on workpieces. They come in various configurations to create different thread profiles, including internal and external threads.

- Features:
- Thread-forming geometry.
- Available in various thread pitches and sizes.
- Suitable for both internal and external threading.
- Often used for creating precise threads in materials that are difficult to tap.
- Functions:
- Machining threads in threaded holes (internal threads).
- Creating threads on the external surface of workpieces (external threads).
9. Woodruff Cutter
Woodruff cutters, also known as keyseat cutters, are used for cutting keyways in shafts and other cylindrical parts. They have a distinctive “T”-shaped cutting edge and are available in various sizes to match keyway dimensions.
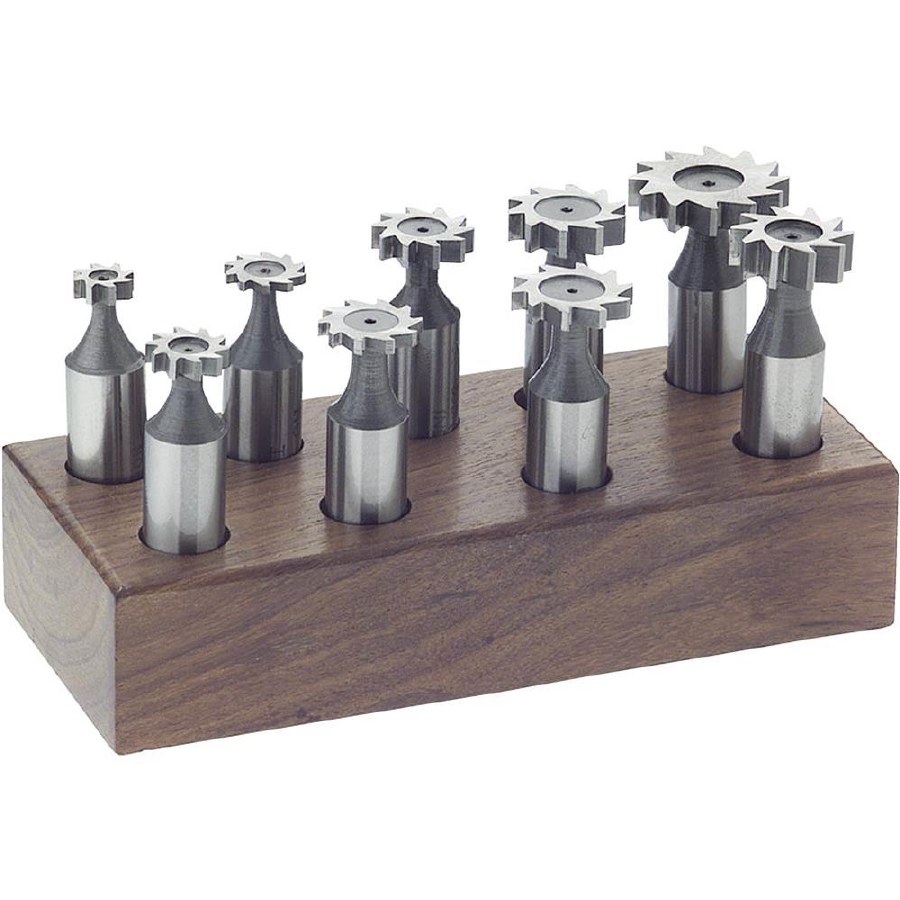

- Features:
- “T”-shaped cutting edge.
- Available in different widths and diameters.
- Used for creating keyways for securing keys and key stock.
- Functions:
- Cutting keyways in shafts and pulleys.
10. Dovetail Cutter
Dovetail cutters are specialized tools used for machining dovetail slots and other angular profiles. They have a unique shape with cutting edges that resemble a dovetail joint.

- Features:
- Dovetail-shaped cutting profile.
- Available in various angles and sizes.
- Suitable for creating dovetail grooves and other angular features.
- Functions:
- Machining dovetail slots for applications such as tool guides and fixtures.
- Creating angular profiles and recesses.
Key Features of Milling Cutters
Milling cutters exhibit various features and characteristics that determine their suitability for specific machining tasks. Understanding these features is essential for selecting the right cutter for the job. Here are some key features to consider –
1. Material Composition
Milling cutters are made from a range of materials, including high-speed steel (HSS), carbide, and various coatings. Carbide cutters are known for their hardness and durability, making them suitable for high-speed machining and abrasive materials. Coatings like TiN (Titanium Nitride) and TiAlN (Titanium Aluminum Nitride) enhance tool life and performance.
2. Number of Cutting Edges
The number of cutting edges on a milling cutter impacts material removal rates and surface finish. Cutters with more cutting edges tend to be more efficient for high-volume material removal, while those with fewer edges may provide a better finish.
3. Cutter Geometry
Cutter geometry, including rake angle, helix angle, and relief angle, affects chip formation, tool life, and cutting forces. Proper cutter geometry selection is crucial for achieving desired machining outcomes.
4. Coating
Coatings on milling cutters improve wear resistance and reduce friction during machining. Coated cutters are preferred for high-speed and high-temperature applications.
5. Shank Type
The shank of the milling cutter determines how it is mounted in the milling machine. Common shank types include straight shank and tapered shank. The choice depends on the machine’s spindle and tool holder.
6. Insert Configuration (for Indexable Cutters)
For indexable milling cutters, the configuration and placement of inserts play a crucial role. Different insert shapes and positions enable various cutting actions, such as high feed rates, heavy cutting, and finishing.
Functions of Milling Cutters
Milling cutters perform a wide range of functions in machining processes, contributing to the creation of intricate and precise workpieces. Let’s explore the primary functions of milling cutters –
1. Material Removal
Milling cutters excel at material removal, making them indispensable in shaping and profiling workpieces. They efficiently remove excess material to achieve the desired shape, dimensions, and surface finish.
2. Surface Finish
Milling cutters can be used to improve the surface finish of workpieces. By selecting the appropriate cutter and machining parameters, operators can achieve smooth and polished surfaces that meet stringent quality standards.
3. Contouring and Profiling
Cutters like ball noses and dovetail cutters are ideal for contouring and profiling tasks. They create complex shapes and curves with precision, making them essential for industries like aerospace and automotive.
4. Keyway and Slot Cutting
Woodruff cutters and slitting saws are designed for cutting keyways, slots, and grooves in workpieces. These cutters ensure tight tolerances and accurate fits for various mechanical components.
5. Thread Machining
Thread mills are dedicated to machining threads in workpieces, eliminating the need for tapping or die threading processes. They produce precise threads in a wide range of materials.
6. Hole Drilling
Some milling cutters, like end mills, can also be used for drilling holes in workpieces. This versatility allows for multifunctional tooling setups, reducing the need for dedicated drilling tools.
Selecting the Right Milling Cutter
Choosing the right milling cutter for a specific machining task is a critical decision that directly impacts the quality and efficiency of the process. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a milling cutter –
1. Material Compatibility
Some materials, such as hardened steel or exotic alloys, may require specialized cutters with specific coatings and geometries.
2. Machining Operation
Determine the machining operation you need to perform, whether it’s roughing, finishing, contouring, or slotting. Different operations may require different cutter types.
3. Workpiece Geometry
The shape and geometry of the workpiece influence the choice of cutter. For complex shapes, such as 3D contours, ball nose or tapered end mills may be preferred.
4. Machine Capability
Ensure that your milling machine can accommodate the chosen cutter. Factors like spindle speed, tool holder compatibility, and machine rigidity should be considered.
5. Tool Life and Cost
Consider the expected tool life and budget constraints. High-performance cutters may offer longer tool life but come at a higher cost.
6. Surface Finish Requirements
For applications requiring a superior surface finish, select cutters designed for finishing operations.
7. Cutting Speed and Feed Rate
Match the cutter’s recommended cutting speed and feed rate to the machining conditions. Adjusting these parameters optimizes tool performance and prolongs tool life.
Manufacturers and Suppliers of Milling Cutters
Here are 10 well-known manufacturers and suppliers of milling cutters –
- Sandvik Coromant: Sandvik Coromant is a global leader in cutting tools and tooling systems, including milling cutters for various machining applications.
- Kennametal: Kennametal offers a wide range of cutting tools, including milling cutters, for industries such as aerospace, automotive, and energy.
- Seco Tools: Seco Tools provides high-quality milling cutters and machining solutions for precision engineering and manufacturing industries.
- Iscar: Iscar is a renowned manufacturer of cutting tools, including milling cutters, designed for machining a wide range of materials.
- Walter Tools: Walter Tools specializes in precision cutting tools and offers a comprehensive selection of milling cutters for different applications.
- OSG Corporation: OSG Corporation is known for its cutting tool solutions, including end mills and milling cutters, used in various industries.
- Ingersoll Cutting Tools: Ingersoll Cutting Tools offers a broad range of milling cutters and cutting tool solutions for metalworking and other industries.
- MAPAL: MAPAL is a leading manufacturer of precision tools, including milling cutters, for industries like automotive, aerospace, and medical technology.
- Sumitomo Electric Hardmetal: Sumitomo Electric Hardmetal produces a variety of milling cutters and cutting tools for machining operations.
- Niagara Cutter: Niagara Cutter specializes in end mills and milling cutters, offering high-performance cutting solutions for a wide range of applications.
Please verify the current status, product offerings, and contact information for these manufacturers and suppliers based on your specific milling cutter requirements. Additionally, consider reaching out to them directly for inquiries and to ensure they can meet your needs.
Maintenance and Care
To ensure the longevity and performance of milling cutters, proper maintenance and care are essential. Here are some tips for maintaining milling cutters:
- Keep cutters clean and free from chips, debris, and coolant residue.
- Periodically inspect cutters for wear, damage, or chipping of cutting edges.
- Store cutters in a dry and clean environment to prevent corrosion.
- Follow manufacturer recommendations for sharpening or replacing inserts.
- Use appropriate cutting fluid or coolant to control heat and extend tool life.
Conclusion
Milling cutters are indispensable tools in the world of machining, enabling the creation of precise and intricate workpieces across various industries. Understanding the types, features, and functions of milling cutters is crucial for selecting the right tool for the job and achieving optimal machining outcomes. Whether you’re facing complex 3D profiling or simple slot cutting, there’s a milling cutter designed to meet your needs. With the right knowledge and tool selection, you can unlock the full potential of milling technology and elevate your machining capabilities.
FAQ’s
What is a Milling Tool Used for?
A milling tool, also known as a milling cutter or end mill, is a versatile cutting tool used in machining operations to remove material from a workpiece. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of what milling tools are used for –
Step 1: Material Removal
Milling tools are primarily used for material removal from the surface of a workpiece.
Step 2: Create Flat Surfaces
They are employed to create flat and smooth surfaces on workpieces.
Step 3: Contouring
Milling tools with specific geometries can contour and shape workpieces, creating intricate and complex shapes.
Step 4: Drilling Holes
Some milling tools can be used for drilling holes in workpieces, especially for non-standard or large hole sizes.
Step 5: Slot Cutting
Milling cutters can cut slots or grooves in workpieces, used for creating keyways, T-slots, and other recesses.
Step 6: Face Milling
Face milling tools are used for machining the top surface of a workpiece, producing smooth and flat surfaces.
Step 7: Thread Milling
Specialized milling cutters are designed for threading operations, creating external and internal threads.
Step 8: Profile Milling
Profile milling tools are used to create complex profiles and shapes on workpieces, important in the production of gears and camshafts.
Step 9: Helical Interpolation
Milling tools can perform helical interpolation, producing helical shapes or features, such as screw threads.
Step 10: Roughing and Finishing
Coarse-toothed milling tools are used for roughing, while fine-toothed ones are used for finishing operations.
Step 11: High-Speed Machining
Milling tools are used in high-speed machining for rapid and precise material removal.
Step 12: Engraving
Specialized milling cutters with engraving profiles are used for engraving text, logos, or patterns.
Step 13: Cutting Voids and Pockets
Milling tools are employed for removing material from voids, pockets, and recesses in workpieces.
Step 14: Milling Complex Surfaces
Milling tools with multi-axis capabilities are used for producing highly contoured surfaces.
Step 15: Mold Making
Milling tools play a crucial role in mold making, where precision and detailing are essential.
Step 16: Tool and Die Making
They are extensively used in tool and die-making, shaping dies, molds, and components for manufacturing.
What are Form Milling Cutters used for?
Form milling cutters, also known as form cutters or form-relieved cutters, are specialized cutting tools used for shaping and machining workpieces to specific forms or profiles. These cutters are designed to replicate precise shapes and contours, making them essential in various industries and applications. Here’s what form milling cutters are used for –
Custom Profiles: Form milling cutters are used to create custom profiles and shapes on workpieces. They can replicate intricate contours, including curves, angles, and complex geometries.
Gear Manufacturing: In gear manufacturing, form milling cutters are employed to cut gear teeth with precision. They create the gear’s tooth profile, ensuring accurate meshing with other gears.
Mold Making: Form cutters are widely used in mold making to produce molds with intricate shapes, such as those used for plastic injection molding. They can replicate the desired mold cavity or core shape.
Aerospace Components: Form milling cutters are used in the aerospace industry to machine complex and aerodynamic components, such as aircraft wing profiles, turbine blades, and engine parts.
Automotive Parts: Automotive manufacturers use form milling cutters to shape components like camshafts, transmission gears, and engine components, ensuring precise and efficient performance.
Tool and Die Making: Form cutters are crucial in tool and die making, where they shape dies, punches, and other components used in manufacturing processes.
Medical Devices: The medical device industry uses form milling cutters to manufacture intricate and custom-shaped medical implants and devices.
Artistic and Decorative Work: Form milling cutters are used in artistic and decorative metalworking to create unique and aesthetically pleasing designs on sculptures, architectural details, and custom metalwork.
Prototyping: Form cutters are essential in prototype development, enabling the rapid and accurate creation of prototype parts and components with specific shapes and profiles.
Woodworking: In woodworking, form milling cutters are used to shape and contour wooden workpieces, allowing for precise and intricate designs in furniture and cabinetry.
Jewelry Manufacturing: Jewelry makers use form-milling cutters to create custom-designed pieces with intricate patterns, shapes, and settings.
Engraving: Form milling cutters can be used for engraving text, logos, and patterns on various materials, including metal, plastic, and wood.
