Epoxy resins, often referred to as epoxies, are a family of versatile polymers with a wide range of applications across various industries. These resins are known for their exceptional adhesive properties, strength, durability, and resistance to a variety of environmental factors. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into epoxy resins, uncovering their properties, applications, and the myriad ways they contribute to modern manufacturing and everyday life.
Understanding
Epoxy resins are thermosetting polymers, which means they undergo a chemical reaction to harden and cannot be re-melted once cured. This characteristic makes them highly durable and heat-resistant. Epoxy resins are created by mixing an epoxy monomer with a curing agent, which initiates the curing process. The resulting material is strong, rigid, and possesses a remarkable set of properties.
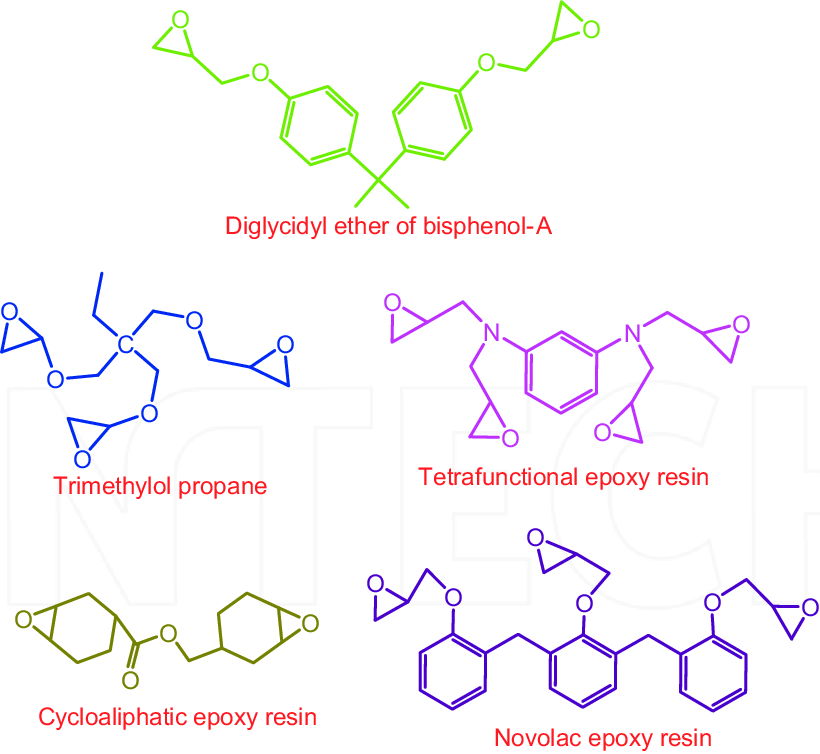
Types of Epoxy Resins
Some common types are –
- Standard Epoxy Resins: These are the most common and versatile epoxy resins. They offer a balance of strength, durability, and adhesion and are used in various applications, including coatings, adhesives, and general-purpose bonding.
- Cycloaliphatic Epoxy Resins: These resins are known for their superior UV resistance and are often used in outdoor applications. They are less prone to yellowing and degradation when exposed to sunlight.
- Novolac Epoxy Resins: Novolac epoxy resins are highly chemical-resistant and are commonly used in industrial settings where exposure to harsh chemicals is a concern, such as in chemical storage tanks and pipelines.
- Water-Based Epoxy Resins: These environmentally friendly epoxy resins use water as a solvent, making them less toxic and more suitable for indoor applications. They are often used for decorative flooring and coatings.
- Bio-Based Epoxy Resins: These resins use renewable materials like soybeans or sugarcane, reducing reliance on petroleum-based resources and promoting sustainability. They are gaining popularity in eco-friendly applications.
- Epoxy Adhesive Resins: Designed for high-strength bonding, epoxy adhesive resins are commonly used in the construction, automotive, and aerospace industries for joining materials together.
- Epoxy Coating Resins: These are formulated for protective coatings and can be used on surfaces like concrete or metal. They provide a durable and attractive finish with resistance to chemicals and wear.
- Clear Epoxy Resins: Often used in art and craft projects, clear epoxy resins offer exceptional clarity and are ideal for encapsulating objects, creating glossy coatings, or crafting resin jewelry.
- High-Temperature Epoxy Resins: These are engineered to withstand extreme heat and are used in applications like aerospace, automotive, and electronics where temperature resistance is critical.
Key Properties
Epoxy resins are celebrated for their remarkable properties, which make them suitable for a wide range of applications:
1. Adhesive Strength
Epoxy resins are renowned for their excellent adhesive properties. They can bond to a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, glass, and wood, creating durable and long-lasting connections.
2. High Strength and Durability
Epoxy resins are exceptionally strong and can withstand heavy loads, making them ideal for structural applications. They also have remarkable durability, ensuring the longevity of bonded materials.
3. Chemical Resistance
Epoxies are highly resistant to chemicals, making them suitable for applications in harsh environments, such as chemical storage tanks and industrial equipment.
4. Thermal Stability
Epoxy resins can withstand high temperatures, which makes them ideal for use in applications where other materials might deform or weaken.
5. Electrical Insulation
Due to their electrical insulating properties, epoxy resins are commonly used in the production of electrical and electronic components, providing protection and insulation.
6. Low Shrinkage
Epoxies exhibit minimal shrinkage during the curing process, ensuring a precise fit when used for molding and casting applications.
7. Water Resistance
Epoxy resins are water-resistant, which is particularly advantageous in marine applications, as well as for coatings and sealants.
Applications
Thanks to their versatile properties, epoxy resins find application in a wide array of industries and sectors. Here are some of the key applications of epoxy resins:
1. Construction and Building
In the construction industry, epoxy resins are used for bonding, repairing concrete structures, and as a protective coating for floors. They provide durability, chemical resistance, and a polished finish.
2. Aerospace and Aviation
Epoxy composites are utilized in aircraft and spacecraft construction due to their lightweight, high-strength characteristics. They play a critical role in enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing the overall weight of aircraft.
3. Electrical and Electronics
Epoxy resins are widely used for encapsulating and insulating electronic components, ensuring electrical safety and protection against environmental factors.
4. Marine Industry
Due to their exceptional water resistance, epoxies are employed in boat building, as well as for repairing and protecting marine vessels from the corrosive effects of saltwater.
5. Automotive Sector
In the automotive industry, epoxy resins are used for manufacturing lightweight composite parts and adhesives for bonding various vehicle components.
6. Art and Crafts
Epoxy resins have gained popularity in the world of arts and crafts. Artists use them for creating intricate resin art, jewelry, and decorative items due to their clarity and self-leveling properties.
7. Medical Devices
Epoxy resins play a critical role in medical devices, providing biocompatible coatings and adhesives used in healthcare applications such as dental work and prosthetics.
8. Woodworking
Epoxy resins are employed for stabilizing and preserving wood, creating striking, transparent wood finishes, and crafting custom wood items.
9. Wind Energy
Wind turbine blades are often made from epoxy composites due to their lightweight, durable, and aerodynamic properties.
10. Aerospace Industry
Epoxy composites are used to manufacture parts for spacecraft, thanks to their lightweight yet robust nature.
Pros & Cons
Pros of Epoxy Resins
- Strong Bonding: Epoxy resins create exceptionally strong and durable bonds, making them ideal for a wide range of applications, from construction to woodworking.
- Chemical Resistance: They are highly resistant to chemicals, making them suitable for use in harsh environments, such as chemical storage tanks.
- Durability: Epoxy resins are known for their long-lasting performance, ensuring the longevity of bonded materials.
- Thermal Stability: They can withstand high temperatures without deforming or weakening, making them suitable for various applications, including those with heat exposure.
- Electrical Insulation: Epoxy resins provide excellent electrical insulation, making them valuable for use in electrical and electronic components.
- Low Shrinkage: They exhibit minimal shrinkage during curing, ensuring a precise fit in molding and casting applications.
- Water Resistance: Epoxy resins are water-resistant, making them suitable for marine applications and as protective coatings and sealants.
Cons of Epoxy Resins
- Curing Time: Epoxy resins require specific curing times, and some formulations may take longer to cure, which can be a drawback in time-sensitive projects.
- Sensitivity to Temperature: The curing process of epoxy resins can be sensitive to temperature, requiring controlled conditions for optimal results.
- Health and Safety Concerns: Epoxy resin fumes and skin contact can cause health issues, so proper safety precautions, such as working in well-ventilated areas and using protective gear, are essential.
- Pot Life: Epoxy resins have a limited pot life, meaning they can only be used for a certain amount of time after mixing, which can be a constraint for larger projects.
- Complex Mixing: Accurate mixing of epoxy and curing agents is crucial for proper curing. Deviations can result in weak bonds or incomplete curing.
- UV Sensitivity: Some epoxy resins may degrade when exposed to UV light over time. UV-resistant formulations are available but may be necessary for outdoor applications.
- Cleanup and Removal: Cured epoxy resin can be challenging to remove from surfaces or tools and often requires mechanical methods or special solvents.
The Role of Epoxy Resins in Sustainability
Epoxy resins are also making strides in sustainability and eco-friendliness. The formulation of bio-based epoxy resins, using renewable materials like soybeans or sugarcane, is reducing the industry’s reliance on petroleum-based resources. This trend aligns with the growing demand for environmentally friendly materials and processes.
Epoxy Resin Flooring: Step-by-Step Process
Epoxy resin flooring is a popular choice for both residential and industrial spaces due to its durability, chemical resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Here’s a step-by-step guide to installing epoxy resin flooring –
Step 1: Surface Preparation
- Clean the Surface: Ensure the substrate (concrete or existing flooring) is clean, free of dirt, dust, and contaminants. Any imperfections or cracks should be repaired.
- Etching or Grinding: For better adhesion, etch the surface using acid or mechanically grind it to create a rough texture. This step promotes epoxy bonding.
Step 2: Primer Application
- Apply a Primer: A thin layer of epoxy primer is applied to the prepared surface. This helps seal the substrate and provides a strong base for the epoxy coating to adhere to. Allow the primer to cure according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Step 3: Epoxy Coat Application
- Mix Epoxy Resin: Prepare the epoxy resin by thoroughly mixing the resin and hardener according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Be sure to mix it well to ensure proper curing.
- Application: Apply the mixed epoxy resin onto the surface using a roller or brush. Work in small sections to ensure an even coat. Pay attention to edges and corners. For decorative effects, colored flakes or other additives can be applied during this step.
Step 4: Self-Leveling and Spreading
- Self-Leveling: Epoxy resins are self-leveling to some extent. Use a roller or squeegee to help spread the epoxy evenly and ensure it reaches all areas of the surface.
Step 5: Allow Curing Time
- Curing: The epoxy coat needs time to cure, typically for 24 to 72 hours, depending on the specific product and conditions. The curing time allows the epoxy to harden and achieve its full strength.
Step 6: Optional Additional Coats
- Additional Coats: Depending on the desired thickness and finish, additional epoxy coats can be applied. For a high-gloss finish, a clear topcoat is often used to enhance the flooring’s aesthetics and durability.
Step 7: Final Inspection and Maintenance
- Inspect the Flooring: Once the epoxy resin flooring has fully cured, inspect it for any imperfections. Touch up any areas that may require additional attention.
- Maintenance: Epoxy resin flooring is relatively low maintenance. Regular cleaning with mild detergents and gentle scrubbing will help maintain its appearance and extend its lifespan.

Conclusion
Epoxy resins, with their impressive combination of strength, durability, adhesive properties, and resistance to various environmental factors, have become indispensable in numerous industries. They are the unsung heroes behind the structures we build, the technology we rely on, and the art we create.
As the world continues to seek innovative solutions that prioritize sustainability, epoxy resins are evolving to meet these demands through bio-based formulations and eco-friendly applications. Their versatility and adaptability ensure they will remain a key player in the manufacturing and creative processes, contributing to a more sustainable and advanced future. Epoxy resins truly deserve the spotlight, as they continue to unveil new possibilities in materials science and technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are epoxy resins?
Epoxy resins are thermosetting polymers that are created by mixing an epoxy monomer with a curing agent. They harden or cure to form a strong, durable, and chemically resistant material.
What are the key properties of epoxy resins?
Epoxy resins are known for their excellent adhesive strength, high strength and durability, chemical resistance, thermal stability, electrical insulation properties, low shrinkage, and water resistance.
Where are epoxy resins commonly used?
Epoxy resins find applications in various industries, including construction, aerospace, electrical and electronics, marine, automotive, art and crafts, medical devices, woodworking, wind energy, and aerospace, among others.
How do epoxy resins cure?
Epoxy resins cure through a chemical reaction between the epoxy monomer and a curing agent. This reaction is initiated by mixing the two components and often requires a specific curing time and temperature.
What is the difference between epoxy resins and other adhesives, like super glue or wood glue?
Epoxy resins differ from common adhesives like superglue or wood glue in their superior adhesive strength, durability, and chemical resistance. They are designed for bonding a wide range of materials and provide stronger, long-lasting connections.
Are epoxy resins safe to use for art and craft projects?
Epoxy resins can be safe for art and craft projects when used according to instructions. It’s essential to work in a well-ventilated area, wear protective gear, and follow safety guidelines to minimize exposure to fumes and skin contact.
Can epoxy resins be used for outdoor applications?
Yes, epoxy resins are suitable for outdoor applications, as they offer excellent weather and UV resistance. However, some formulations may require additional UV protection for prolonged exposure to sunlight.
Are there eco-friendly or bio-based epoxy resins available?
Yes, there are eco-friendly epoxy resin formulations that use bio-based materials, such as soybeans or sugarcane, reducing reliance on petroleum-based resources and aligning with sustainability goals.
What is the shelf life of epoxy resins?
The shelf life of epoxy resins varies depending on the specific product and manufacturer. It’s essential to check the manufacturer’s recommendations and use the resin within the recommended timeframe for optimal performance.

