All About Rotational Molding, its process, Technologies used, Rotational Molding machine, 3 types of rotational molding , advantages, disadvantages and applications of rotational molding.

Water tank a Rotational Molding Product
Introduction
Rotational molding, is generally known by its common name in market as rotomolding or rotational casting. It is a manufacturing process which is basically used to make hollow plastic products. It is a specialized technique that involves heating, melting, and rotating a mold to produce three-dimensional, seamless plastic parts. This process is widely employed for manufacturing large, complex, and durable objects, ranging from water tanks and storage containers to automotive components and playground equipment.
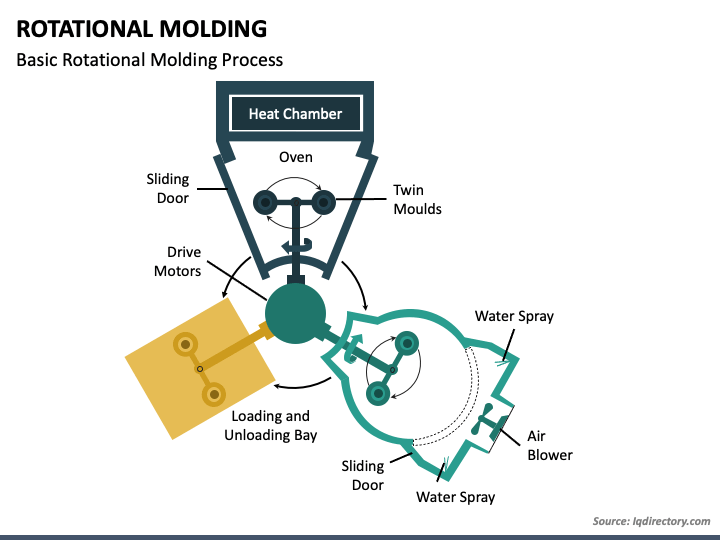
Rotational Molding Process
The rotational molding process begins with a mold, usually made of aluminum or steel, which is shaped like the desired end product. The mold is loaded with a predetermined amount of powdered thermoplastic material, such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), or polyvinyl chloride (PVC). The mold is then closed, and the heating phase begins.
The mold is heated in an oven or a specialized rotational molding machine, causing the plastic powder to melt and coat the inner walls of the mold. As the mold rotates bi-axially along two perpendicular axes, the molten plastic spreads evenly, creating a uniform layer. The rotation continues during the cooling phase to ensure that the plastic retains its shape as it solidifies.
After the cooling process is complete, the mold is opened, and the finished product is removed. Depending on the complexity of the design, multiple molds or inserts can be used to create additional features, such as handles or threaded openings, in the final product.
Types of Rotational Molding
There are mainly 3 types of rotational molding and they are explained below –
- 1. Traditional Rotational Molding : Traditional rotational molding is the most common and widely used method. In this process, a single mold is loaded with plastic powder, heated, and rotated bi-axially. The mold rotates slowly and continuously on two perpendicular axes, allowing the molten plastic to spread and evenly coat the inner walls of the mold. The rotation continues during the cooling phase until the plastic solidifies. Once the cooling is complete, the mold is opened, and the finished product is removed. Traditional rotational molding is suitable for producing large and complex parts with uniform wall thickness.
- 2. Shuttle Rotational Molding : Shuttle rotational molding involves the use of multiple molds or stations that shuttle back and forth between heating, cooling, and loading/unloading positions. The molds are loaded with plastic powder, heated, and rotated to distribute the molten plastic within the mold. After the heating and cooling phases, the molds are shuttled to the unloading position, and the finished products are removed. Meanwhile, the empty molds are moved to the loading position to start a new cycle. Shuttle rotational molding allows for increased production efficiency by reducing the cooling time and enabling simultaneous loading and unloading operations.
- 3. Carousel Rotational Molding : Carousel rotational molding, also known as multiple-arm rotational molding, utilizes a central rotating carousel with multiple arms or spokes radiating from it. Each arm holds a separate mold, allowing multiple molds to be processed simultaneously. The carousel rotates, bringing each mold through the heating, cooling, and loading/unloading positions in a sequential manner. This method offers high production output and is ideal for manufacturing small to medium-sized products with consistent quality. Carousel rotational molding is commonly used for high-volume production runs.
Technologies & Equipment’s Usages
Rotational molding utilizes various technologies and equipment to ensure the efficient and precise manufacturing of plastic products. Here are some key technologies commonly employed in rotational molding –
Rotational Molding Machines
Rotational molding machines are the primary equipment used in the rotational molding process. These machines consist of a hollow oven or chamber, a system for rotating the molds, and controls for temperature, time, and speed. The machines can be either independent units or integrated into a carousel or shuttle system, depending on the production requirements. Modern rotational molding machines often feature advanced automation and programmable controls to optimize the molding process and ensure consistent quality.

Mold Design and Manufacturing
Mold design and manufacturing play a crucial role in rotational molding. Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software is used to create 3D models of the desired product, which are then converted into mold designs. Mold materials are typically aluminum or steel, chosen for their durability and heat transfer properties. Advanced machining techniques, such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining, are employed to create precise molds with intricate features and details.
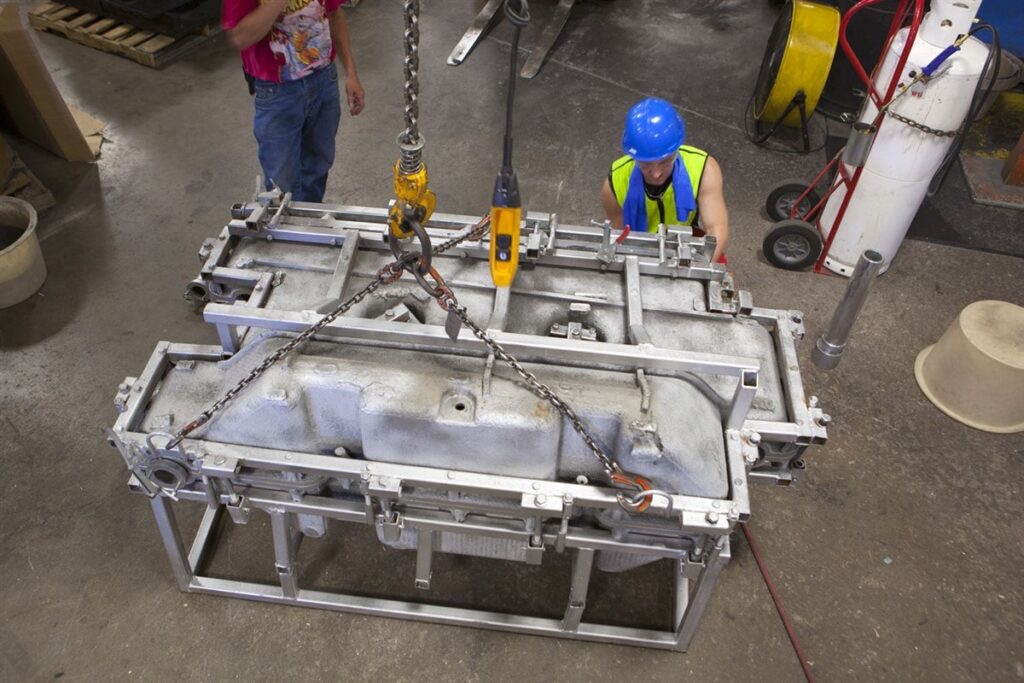

Heating and Cooling Systems
Heating is a critical step in rotational molding, and different heating systems are used to achieve uniform heating of the molds. Convection ovens, which circulate hot air, are commonly used to heat the molds. In some cases, infrared heating systems or other specialized heating methods may be employed. Cooling systems, such as fans or water sprays, are used during the cooling phase to accelerate solidification and maintain dimensional stability.
Powder Handling and Dispensing
Rotational molding involves the use of powdered thermoplastic materials. Efficient powder handling and dispensing systems are employed to accurately measure and deliver the required amount of plastic powder into the mold. These systems ensure consistent material distribution and minimize wastage.
Mold Release Agents
Mold release agents are substances applied to the mold surface to prevent the molten plastic from sticking or adhering to the mold during the molding process. These agents can be in the form of powders, sprays, or liquids and are selected based on the specific plastic material being used. Mold release agents aid in easy demolding and help maintain the surface finish of the molded product.
Quality Control and Testing
To ensure the quality and integrity of rotational molded products, various testing and quality control methods are employed. These may include non-destructive testing techniques, such as visual inspection, dimensional checks, and pressure testing, to verify the product’s conformance to specifications. Additional tests, such as impact resistance, tensile strength, and environmental durability testing, may also be performed to assess the product’s performance and durability.
Applications of Rotational Molding
Rotational molding finds a wide range of applications across various industries. Its ability to produce large, seamless, and structurally robust plastic products makes it suitable for diverse purposes. Here are some common applications of rotational molding –
- Tanks and Containers : Rotational molding is extensively used for manufacturing tanks and containers for storing liquids and solids. These include water tanks, chemical storage tanks, fuel tanks, agricultural storage bins, waste containers, and industrial drums. Rotational molding allows for the production of large-capacity, durable, and corrosion-resistant containers.
- Automotive Components : Many automotive components can be efficiently produced through rotational molding. Examples include fuel tanks, air ducts, fenders, wheel arches, bumpers, and interior trim parts. Rotational molding offers design flexibility and allows for the integration of multiple features into a single part, reducing the need for assembly and enhancing overall efficiency.
- Recreational and Sports Equipment : Rotational molding is widely used in the production of recreational and sports equipment, such as kayaks, canoes, playground equipment, slides, swing sets, and ballistics training aids. The process allows for the creation of strong and durable products with complex shapes and designs that meet the safety and performance requirements of these applications.
- Furniture and Outdoor Living : Rotational molding is employed to manufacture outdoor furniture, including chairs, tables, benches, and planters. The process enables the production of weather-resistant, UV-stable, and low-maintenance furniture pieces. Additionally, rotational molding is used to create outdoor storage containers, coolers, and decorative elements for landscaping and garden applications.
- Industrial and Material Handling Equipment : Rotational molding is employed to manufacture a variety of industrial and material handling equipment, including pallets, bins, containers, industrial enclosures, and protective cases. The process ensures that these products are durable, impact-resistant, and capable of withstanding harsh working environment.
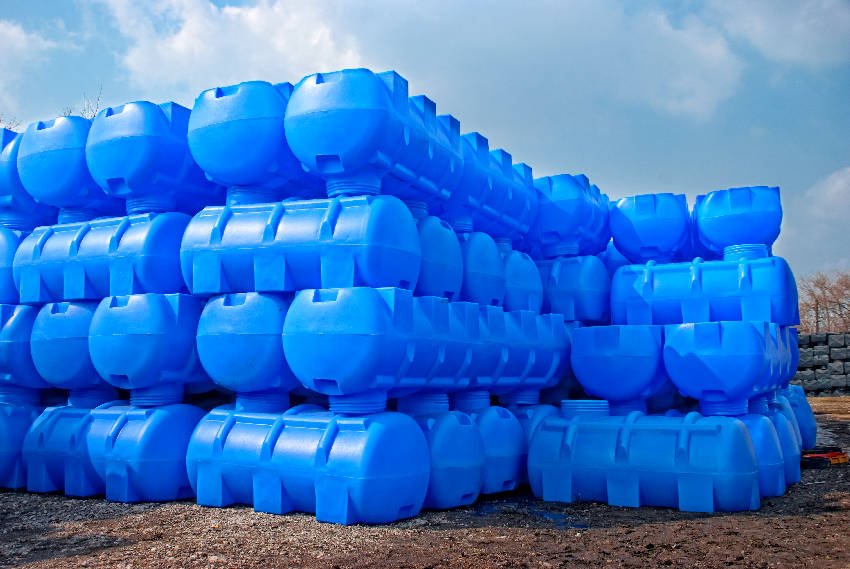

Rotational Molding Poducts
Image Credit: Treatstock
Advantages of Rotational Molding
Rotational molding offers several advantages that make it a preferred manufacturing method for a variety of plastic products. Some key advantages of rotational molding include –
- Design Flexibility
- Seamless and Stress-Free Products
- Large Part Capability
- Cost-Effective for Low-Volume Production
- Material Versatility
- Uniform Wall Thickness
- Enhanced Product Properties
- Reduced Tooling and Setup Time
Disadvantages of Rotational Molding
While rotational molding offers numerous advantages, it also has some disadvantages that should be considered in certain manufacturing scenarios. Here are some key disadvantages of rotational molding –
- Longer Cycle Time
- Limited Material Selection
- Variation in Wall Thickness
- Surface Finish Limitations
- Limited Design Complexity
- Material Waste
- High Initial Tooling Cost
Conclusion
Rotational molding process offers numerous advantages and applications in the manufacturing of plastic products. Its design flexibility, ability to produce large and structurally robust parts, and cost-effectiveness for low-volume production make it a preferred choice for various industries. The seamless construction, uniform wall thickness, and material versatility contribute to the durability and performance of rotational molded products.
However, it is important to consider the disadvantages associated with rotational molding, such as longer cycle times, limited material selection, variation in wall thickness, surface finish limitations, design complexity restrictions, material waste, and initial tooling costs. These factors should be carefully evaluated based on specific product requirements and production volume.
Overall, rotational molding offers a versatile and efficient manufacturing process for a wide range of plastic products. Its ability to create complex shapes without seams or joints, along with its strength and durability, makes it an attractive option for industries such as automotive, recreation, furniture, agriculture, and more. With advancements in technology and ongoing process refinements, rotational molding continues to evolve and find new applications, contributing to the production of high-quality plastic products in various industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here some frequently asked questions with there answer I am providing for you, don’t miss them –
What is rotational molding?
It is a manufacturing process which is basically used to make hollow plastic products. It is a specialized technique that involves heating, melting, and rotating a mold to produce three-dimensional, seamless plastic parts. This process is widely employed for manufacturing large, complex, and durable objects, ranging from water tanks and storage containers to automotive components and playground equipment.
What is made from rotational molding?
Water Tanks and Storage Containers, fuel tanks, air ducts, fenders, interior trim part, orthopedic supports, hospital bed components, wheelchair accessories, pallets, bins, containers, agricultural sprayers, animal feeders, irrigation components, septic tanks, wastewater treatment components, display items, safety barriers, pontoons, and industrial housings and many more products are produce from rotational molding process.
What material is used in rotational molding?
Rotational molding mostly uses Polyethylene (PE), Polypropylene (PP), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), Nylon and Cross-linked Polyethylene (PEX).
Why are vent holes important to rotational molding?
Vent holes are essential in the rotational molding process for several reasons –
(1) Air Evacuation. (2) Pressure Equalization. (3) Prevention of Blowouts. (4) Reduction of Surface Imperfections. (5) Enhanced Cooling Efficiency.
What is the max. thickness of plastic on rotational molding?
For small to medium-sized products, typical thicknesses in rotational molding can range from 2 mm to 10 mm. This range is often suitable for applications such as storage containers, automotive components, playground equipment, and furniture.
In cases where larger or more structurally demanding parts are required, the maximum thickness can exceed 10 mm and go up to several centimeters. For example, in the production of large water tanks or industrial storage tanks, the thickness of the plastic can reach 20 mm or more.
What is difference between rotational and injection molding?
Rotational molding and injection molding are two distinct plastic molding processes with notable differences. Here are the key differences between rotational molding and injection molding –
1. Process : Rotational molding involves rotating a mold while heating and cooling it to create a hollow plastic product. The plastic material is loaded as a powdered resin into the mold, which is then heated and rotated to evenly distribute the molten plastic along the inner walls of the mold. In contrast, injection molding uses a stationary mold into which molten plastic material is injected under high pressure. The plastic material is injected into the mold cavity, where it solidifies and forms the desired product.
2. Mold Deign : Rotational molding typically uses simple molds made of aluminum or steel, which can be less expensive compared to injection molding molds. Rotational molds are typically easier to modify or replace, providing greater design flexibility. Injection molding requires more complex molds with multiple components, including cores and slides, to create intricate shapes and features.
3. Product Complexity : Rotational molding is suitable for producing larger, hollow, and more complex-shaped parts. It is well-suited for products with varying wall thicknesses and complex geometries, such as water tanks, playground equipment, and kayaks. Injection molding, on the other hand, is capable of producing intricate and precise parts with tight tolerances, making it suitable for applications requiring high precision and intricate details.
4. Production Volume : Injection molding is commonly used for high-volume production runs due to its faster cycle times and higher production rates. It is ideal for manufacturing large quantities of identical parts consistently. Rotational molding, although capable of high-quality production, typically has longer cycle times and is more suitable for low to medium production volumes or custom-made products.
5. Surface Finish : Injection molding generally provides a smoother and more refined surface finish compared to rotational molding. Rotational molding can result in a textured or slightly rough surface due to the contact between the plastic and the mold. While the surface finish in rotational molding can be improved through post-processing techniques, injection molding typically delivers a higher-quality surface finish right out of the mold.