Introduction
Mold clamps are a critical component in the world of molding, playing a pivotal role in ensuring the efficiency, precision, and safety of the molding process. Whether it’s injection molding, blow molding, or any other type of molding operation, the right choice of mold clamps can significantly impact the quality and success of the final product. In this blog, we will delve into the fundamentals of mold clamps, their various types, applications, benefits, and best practices. By the end of this comprehensive guide, you will have all the knowledge you need to harness the power of mold clamps for successful molding.
What are Mold Clamps?
Mold clamps are mechanical devices used to firmly hold the mold halves together during the molding process. They create a strong and secure connection between the mold plates, preventing any shifting or misalignment while the molten material is injected or shaped. These are typically made of high-quality materials such as steel or stainless steel to withstand the pressure and forces involved in molding operations.

Types of Mold Clamps
There are several types of mold clamps available, each designed to suit specific molding applications. Some common types include –
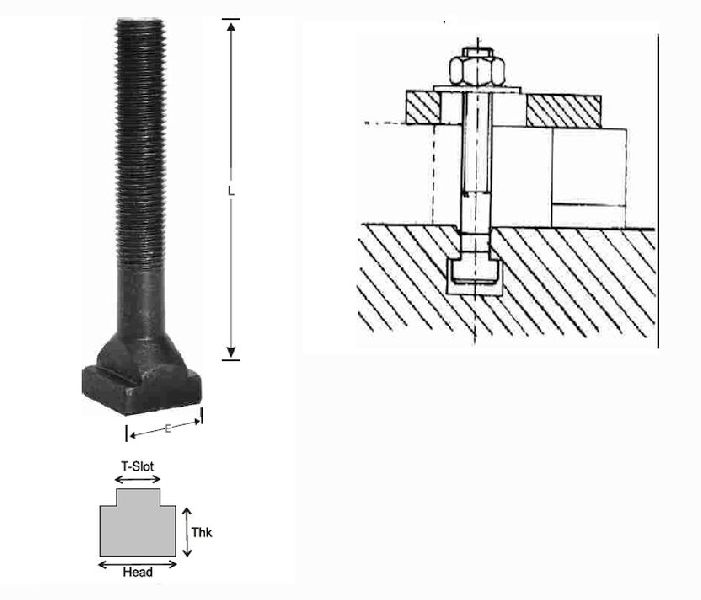
T-Slot Type
T-slot clamps are a popular choice for their versatility and ease of use. They slide into T-shaped slots on the mold plates and can be quickly adjusted to accommodate various mold sizes.
Strap Type
Strap clamps use straps or bands to secure the mold plates tightly. They are well-suited for applications where T-slot configurations are not available or feasible.
Toe Type Clamps
Toe clamps are used when the mold has no T-slots and limited space. They provide a strong, direct clamping force on the mold plates.

Wedge Type Clamps
Wedge clamps use a wedge mechanism to apply pressure and secure the mold halves together. They are commonly used in die-casting applications.

Importance of Mold Clamps in Successful Molding
It plays a crucial role in the molding process for several reasons –

Precise Alignment
Properly tightened mold clamps ensure that the mold plates are perfectly aligned, minimizing defects and improving product consistency.
Safety
It prevents the mold halves from separating during the molding process, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries.
Reduced Downtime
Efficient mold clamps facilitate quick mold changes, leading to reduced downtime and increased productivity.
Improved Product Quality
With stable and secure mold clamping, the molding process can achieve higher precision and produce higher-quality products.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Mold Clamps
Selecting the right clamps for your molding process is essential for optimal performance. Consider the following factors –
Material and Durability
Choose clamps made from high-quality materials that can withstand the forces and temperature variations of the molding process.
Size and Compatibility
Ensure the clamps are the right size and compatible with your mold plates, ensuring a proper fit and alignment.
Clamping Force
The clamping force should be sufficient to securely hold the mold halves together without causing damage.
Ease of Use
Opt for clamps that are easy to install, adjust, and remove, reducing setup time and complexity.
Best Practices for Using Mold Clamps
To maximize the benefits of clamps and ensure successful molding, consider these best practices –
Regular Maintenance
Conduct routine inspections and maintenance of the clamps to identify any signs of wear or damage.
Proper Lubrication
Lubricate the moving parts of the clamps to ensure smooth and consistent clamping action.
Correct Torque
Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for tightening the clamps to the recommended torque levels.
Training and Safety
Train operators in proper mold clamping procedures and safety protocols to avoid accidents and mishaps.
Pros & Cons of Mold Clamps
Pros
Secure Molding Process
It provides a strong and reliable connection between the mold plates, ensuring that they remain securely in place during the molding process. This stability leads to better product quality and reduced defects.
Precision and Consistency
Properly tightened clamps help maintain precise alignment between the mold halves. This alignment ensures consistent product dimensions and reduces variations, resulting in higher-quality finished products.
Versatility
It comes in various types and configurations, making them adaptable to different mold sizes and shapes. This versatility allows manufacturers to use the same mold clamps for multiple molding applications, reducing costs and setup time.
Quick Mold Changes
These are easy to install and adjust to facilitate rapid mold changes. This feature is especially advantageous for manufacturers who need to switch between different molds frequently, leading to increased productivity and reduced downtime.
Operator Safety
It contributes to operator safety by preventing the mold halves from separating during the molding process. This minimizes the risk of accidents and injuries associated with mold misalignment or movement.
Cost-Effectiveness
Investing in high-quality mold clamps can lead to long-term cost savings. These clamps are durable and withstand the stresses of molding operations, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Cons
Initial Setup Complexity
Depending on the type and design of clamps, the initial setup process can be intricate, requiring careful alignment and proper torque application. This complexity may increase setup time and require skilled operators.
Wear and Tear
Over time, clamps can experience wear and tear due to the repetitive nature of molding operations. Regular maintenance and occasional replacements may be necessary to ensure optimal performance.
Mold Damage Risk
If clamps are over-tightened or misused, there is a risk of damaging the mold plates. This can lead to additional expenses for mold repairs or replacements.
Limited Clamping Force Range
Some clamps may have limitations in terms of their clamping force range. This can be a challenge when working with molds that require exceptionally high or low clamping forces.
Compatibility Issues
Clamps need to be compatible with the mold plates’ design and dimensions. If the wrong type of clamp is used or if the mold plates lack suitable mounting features, it may lead to difficulties in achieving proper clamping.
Maintenance Requirements
Clamps, like any mechanical components, require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and extend their lifespan. Failure to perform regular maintenance can lead to decreased efficiency and potentially compromised product quality.
**Mold clamps play a vital role in successful molding operations, providing numerous benefits such as secure mold alignment, improved product quality, and operator safety. While they offer significant advantages, mold clamps also come with some drawbacks, including setup complexity, maintenance requirements, and potential mold damage risks. Manufacturers must carefully select the appropriate mold clamps, follow recommended practices, and conduct regular maintenance to ensure efficient and safe molding processes while mitigating potential challenges. Ultimately, mold clamps remain indispensable tools for achieving precision, consistency, and success in various molding applications.
Applications Of Mold Clamps
Mold clamps find widespread applications in various molding processes, where they play a crucial role in securely holding the mold plates together during the production of different types of products. Some of the primary applications of mold clamps include –
Injection Molding
Mold clamps are extensively used in injection molding, one of the most common and versatile manufacturing processes. They ensure that the mold halves remain tightly sealed during the injection of molten plastic or other materials into the cavity, resulting in accurate and consistent product dimensions.
Blow Molding
In blow molding, mold clamps are essential for securing the two halves of the mold during the formation of hollow plastic products, such as bottles, containers, and automotive components.
Compression Molding
Mold clamps are employed in compression molding, a manufacturing process that involves compressing materials, such as rubber or thermosetting plastics, into specific shapes. The clamps keep the mold plates tightly together to achieve the desired product configuration.
Thermoforming
Thermoforming involves heating a plastic sheet and forming it into a desired shape using a mold. Mold clamps secure the mold halves, ensuring precise molding and efficient cooling of the formed products.
Die Casting
In die casting, mold clamps are used to hold the mold halves in place while the molten metal is injected under pressure to create metal parts with complex shapes and high precision.
Extrusion Molding
Mold clamps are used in extrusion molding to maintain a constant profile shape and dimensions of extruded materials, such as plastic profiles, pipes, and tubes.
Rotational Molding
Mold clamps are employed in rotational molding, where a hollow mold is filled with polymer powder and rotated in an oven until the powder coats the mold’s interior, forming the final product.
Rubber Molding
In rubber molding processes like injection molding of rubber or transfer molding, mold clamps secure the mold halves and allow for precise shaping of rubber components.
Reaction Injection Molding (RIM)
RIM involves the chemical reaction of two liquid components to form a polyurethane or other polymer product. Mold clamps hold the mold together during this reactive process.
Foam Molding
In foam molding processes like foam injection molding or foam compression molding, mold clamps are utilized to shape foam materials into various products.
Conclusion
Mold clamps are an integral part of successful molding operations, impacting product quality, production efficiency, and operator safety. Understanding the different types of mold clamps, their applications, and best practices for their use is crucial for achieving the desired outcomes in molding processes. By investing in high-quality mold clamps and adhering to recommended practices, manufacturers can unlock the full potential of their molding operations and create top-notch products with precision and consistency. Remember, when it comes to molding, a firm grip with the right mold clamps can make all the difference.
I have tried here to answer some questions which are frequently asked/searched on the net & they are –
What is a clamp in injection molding?
A clamp in injection molding is a mechanical device that securely holds the two halves of the mold together during the molding process. It applies the necessary force to keep the mold closed, allowing molten material to be injected into the mold cavity to form the desired product.
What is called a clamp?
In the context of manufacturing and construction, a clamp refers to a device used to hold or secure objects firmly together. Clamps come in various forms, including C-clamps, bar clamps, spring clamps, and more, and are widely used in woodworking, metalworking, welding, and other applications where strong, temporary fastening is needed.
What is a clamp used for?
A clamp is used to securely hold or fasten objects together. It applies pressure to hold workpieces, materials, or components firmly in place during various processes like welding, woodworking, metalworking, molding, and construction, ensuring precise and stable assembly, gluing, cutting, or shaping.
What is a mold clamp?
A mold clamp is a mechanical device used in molding processes, such as injection molding, to firmly hold the two halves of a mold together. It creates a strong and stable connection between the mold plates, ensuring precise alignment during the molding process and improving product quality and consistency.


Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.