Introduction
Injection molding machines are the backbone of modern manufacturing, enabling the production of a wide range of plastic products. However, like any complex machinery, they are susceptible to breakdowns that can halt production and impact quality. In this extensive guide, we’ll explore the top 25 breakdowns that can occur in injection molding machines and provide valuable troubleshooting insights to help you address these issues effectively.
Top 25 Injection Molding Machine Breakdowns
01. Screw and Barrel Wear – Injection Molding Machine Breakdown
Symptoms: Poor material mixing, increased cycle times, reduced quality.
Causes: Continuous use, abrasive materials, high temperatures.
Troubleshooting:
- Measure the wear of the screw and barrel and replace them if necessary.
- Optimize for wear-resistant coatings or materials.
- Adjust processing parameters to accommodate wear-related changes.

02. Nozzle Blockages – Injection Molding Machine Breakdown
Symptoms: Reduced material flow, incomplete fills, poor part quality.
Causes: Residual material buildup, contamination, improper purging.
Troubleshooting:
- Clean and clear nozzle passages regularly.
- Use effective purging compounds to prevent buildup.
- Monitor material quality and filter contaminants.

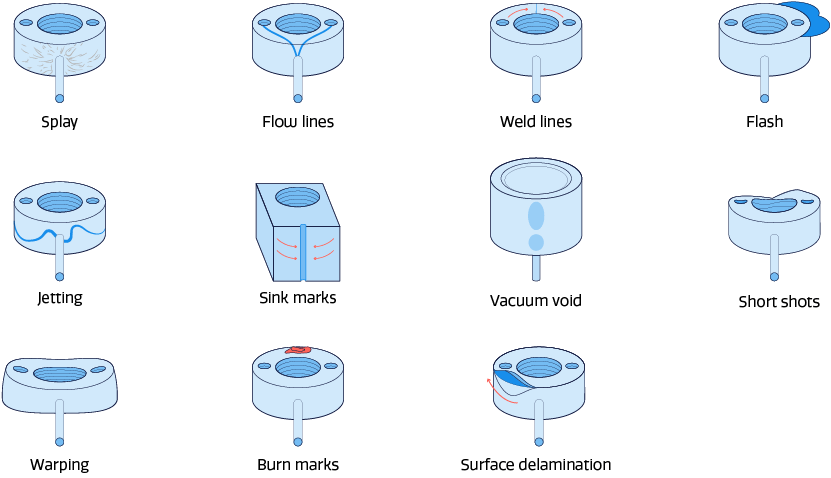
03. Molding Surface Defects
Symptoms: Surface imperfections, sink marks, warping.
Causes: Mold design issues, improper cooling, high injection pressures.
Troubleshooting:
- Analyze the mold design for flow and cooling optimization.
- Adjust injection parameters to reduce pressure and speed.
- Implement a proper mold maintenance regimen.
04. Hydraulic System Failure – Injection Molding Machine Breakdown
Symptoms: Slow operation, erratic movement, leaks.
Causes: Fluid contamination, pump issues, valve blockages.
Troubleshooting:
- Check hydraulic fluid levels and quality; replace if needed.
- Inspect pumps and valves for proper functionality.
- Flush the hydraulic system and replace filters.

05. Electrical Component Failures – Injection Molding Machine Breakdown
Symptoms: Power fluctuations, unresponsive controls, machine errors.
Causes: Wear and tear, electrical surges, faulty components.
Troubleshooting:
- Inspect and replace damaged or worn electrical components.
- Implement surge protection mechanisms.
- Regularly maintain and inspect electrical connections.

06. Material Variation Issues
Symptoms: Inconsistent part dimensions, color variations.
Causes: Inaccurate material blending, moisture content, contamination.
Troubleshooting:
- Ensure proper material handling and storage to prevent moisture absorption.
- Calibrate material blending systems regularly.
- Clean and maintain hoppers and material feed systems.
07. Injection Unit Malfunction – Injection Molding Machine Breakdown
Symptoms: Inaccurate shot size, material leakage, uneven melt.
Causes: Worn-out or misaligned components, blocked nozzle, sensor issues.
Troubleshooting:
- Inspect and clean the injection unit, including nozzles and barrels.
- Check sensors and replace if faulty.
- Calibrate the injection settings according to manufacturer guidelines.
08. Controller Errors – Injection Molding Machine Breakdown
Symptoms: Display errors, incorrect parameters, unresponsive controls.
Causes: Software glitches, communication errors, electrical issues.
Troubleshooting:
- Restart the machine and reinitialize the controller.
- Update or reinstall software as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Check and secure all electrical connections.
09. Ejector System Problems
Symptoms: Sticking ejector pins, incomplete ejection, misalignment.
Causes: Wear and tear, lack of lubrication, mechanical issues.
Troubleshooting:
- Lubricate ejector system components regularly.
- Inspect pins, plates, and guides for damage and replace them if needed.
- Ensure proper alignment of the ejector system.
10. Heater and Thermocouple Failures – Injection Molding Machine Breakdown
Symptoms: Inconsistent temperature control, material degradation.
Causes: Worn-out heaters, damaged thermocouples, electrical issues.
Troubleshooting:
- Replace faulty heaters and thermocouples.
- Verify the accuracy of temperature readings using a separate thermometer.
- Look for damage or loose connections in the wiring and connectors.
11. Injection Pressure Instabilities – Injection Molding Machine Breakdown
Symptoms: Variations in part dimensions, inconsistencies in part quality.
Causes: Pressure sensor inaccuracies, hydraulic fluctuations, mold issues.
Troubleshooting:
- Calibrate pressure sensors and ensure accurate readings.
- Inspect hydraulic components for leaks or malfunctions.
- Verify proper mold venting and cooling to maintain stable pressure.
12. Cooling System Failures – Injection Molding Machine Breakdown
Symptoms: Part warping, cycle time variations, inconsistent cooling.
Causes: Clogged cooling channels, malfunctioning pumps, insufficient cooling.
Troubleshooting:
- Clean and flush cooling channels regularly.
- Inspect and maintain cooling pumps and valves.
- Optimize cooling channel design for uniform heat dissipation.
13. Part Sticking to Mold
Symptoms: Difficulty in part ejection, potential mold damage.
Causes: Poor mold release agent application, inadequate mold venting.
Troubleshooting:
- Apply suitable mold release agents uniformly.
- Optimize mold venting to prevent air entrapment.
- Inspect the ejection system for proper alignment and functionality.
14. Excessive Flashing
Symptoms: Excess material around part edges, decreased part quality.
Causes: Mold misalignment, excessive injection pressure, worn mold components.
Troubleshooting:
- Inspect and align mold components properly.
- Reduce injection pressure to prevent material leakage.
- Repair or replace worn mold components causing flashing.
15. Screw Slippage – Injection Molding Machine Breakdown
Symptoms: Inconsistent material feed, reduced shot size accuracy.
Causes: Worn screw threads, inadequate torque, poor material quality.
Troubleshooting:
- Inspect screw threads for wear and replace if necessary.
- Properly torque the screw to prevent slippage.
- Use high-quality material to avoid wear-related issues.
16. Gas Trap Issues – Injection Molding Machine Breakdown
Symptoms: Bubbles or voids in parts, poor surface finish.
Causes: Poor venting design, and improper injection profile.
Troubleshooting:
- Optimize mold design for proper gas venting.
- Adjust injection profiles to prevent material entrapment.
- Use venting aids or techniques to release trapped gases.
17. Material Degradation – Injection Molding Machine Breakdown
Symptoms: Changes in material properties, and reduced part strength.
Causes: Overheating, excessive shear, prolonged residence time.
Troubleshooting:
- To avoid overheating, optimize the melt temperature and injection speed.
- Minimize residence time by adjusting processing parameters.
- Use materials with better thermal stability for prolonged runs.
18. Short Shot – Injection Molding Machine Breakdown
Symptoms: Incomplete filling of mold, undersized parts.
Causes: Insufficient material, cold runners, inadequate injection pressure.
Troubleshooting:
- Adjust material feed settings to ensure complete filling.
- Ensure proper gate and runner design for optimal flow.
- Increase injection pressure to achieve complete mold filling.
19. Part Warpage – Injection Molding Machine Breakdown
Symptoms: Distorted part geometry, poor fitment.
Causes: Uneven cooling, inadequate holding pressure, poor ejection timing.
Troubleshooting:
- Optimize cooling channel layout for uniform cooling.
- Adjust holding pressure to prevent premature part release.
- Time ejection properly to avoid warpage during ejection.
20. Uneven Shrinkage – Injection Molding Machine Breakdown
Symptoms: Non-uniform part dimensions, variations in part quality.
Causes: Incorrect cooling, improper gate design, and uneven material distribution.
Troubleshooting:
- Ensure uniform cooling and proper mold temperature control.
- Optimize gate design for balanced material flow.
- Adjust material injection and packing settings for even distribution.
21. Screw Breakage – Injection Molding Machine Breakdown
Symptoms: Sudden stoppage, unusual noises, incomplete material feeding.
Causes: Overloading, material degradation, wear and tear.
Troubleshooting:
- Monitor material consumption to avoid overloading.
- Use high-quality and suitable materials for the process.
- Inspect and replace worn or damaged screws promptly.
22. Hydraulic Fluid Contamination – Injection Molding Machine Breakdown
Symptoms: Erratic operation, increased friction, reduced fluid quality.
Causes: Foreign particles, degraded oil, improper maintenance.
Troubleshooting:
- Regularly monitor hydraulic fluid quality and replace if contaminated.
- Implement proper filtration systems to prevent foreign particle entry.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for hydraulic fluid change and maintenance.
23. Mold Release Problems – Injection Molding Machine Breakdown
Symptoms: Difficulty in ejecting parts from the mold, part sticking.
Causes: Inadequate mold release agents, improper ejection system.
Troubleshooting:
- Apply mold-release agents uniformly and as recommended.
- Adjust ejection system settings to ensure smooth part release.
- Optimize mold surface finish for better release properties.
24. Excessive Cycle Time – Injection Molding Machine Breakdown
Symptoms: Prolonged production cycles, reduced efficiency.
Causes: Inefficient cooling, slow ejection, suboptimal parameters.
Troubleshooting:
- Optimize cooling system design for quicker heat dissipation.
- Adjust ejection settings and optimize ejection system design.
- Review injection parameters to reduce unnecessary delays
25. Mechanical Wear and Tear – Injection Molding Machine Breakdown
Symptoms: Increased noise levels, reduced performance, erratic operation.
Causes: Continuous use, lack of maintenance, aging components.
Troubleshooting:
- Regularly inspect machine components for wear and damage.
- Implement a comprehensive maintenance schedule to address wear.
- Replace worn or damaged parts promptly to avoid further complications.
Conclusion
Navigating breakdowns in injection molding machines demands a blend of expertise, proactive maintenance, and problem-solving skills. Understanding the root causes of these common issues and implementing effective troubleshooting strategies is crucial for maintaining smooth operations and minimizing production downtime. By addressing breakdowns promptly and adhering to best practices, manufacturers can optimize the performance of their injection molding machines, ensure consistent product quality, and ultimately drive their businesses towards success in the competitive manufacturing landscape.
FAQ’s
What are the 3 main parts of Injection Molding Machine?
The three main parts of an injection molding machine are –
Injection Unit: This part is responsible for melting and injecting the plastic material into the mold. It includes components like the hopper (where plastic pellets are stored), the barrel (where the plastic is melted), the screw (which moves the plastic forward and mixes it), and the nozzle (which delivers the melted plastic into the mold).
Clamping Unit: The clamping unit holds the mold halves together during the injection and cooling processes. It consists of the stationary platen, the moving platen, and the tie bars that connect them. The mold is attached to these platens, and the clamping unit provides the force necessary to keep the mold closed with high pressure while the plastic is injected and cooled.
Control Unit: The control unit manages and regulates the entire injection molding process. It includes the human-machine interface (HMI), which allows operators to set and monitor various parameters such as temperature, pressure, injection speed, and cycle time. The control unit also houses the programmable logic controller (PLC), which coordinates and controls the machine’s movements, actions, and safety features.
These three main parts work together to execute the injection molding process efficiently and produce high-quality plastic parts.
What are the basic parts of Injection Molding Machine?
The basic parts of an injection molding machine include –
Injection Unit:
Hopper: The container for plastic pellets or resin.
Barrel: A heated cylinder where plastic pellets are melted and mixed using a rotating screw.
Screw: Moves forward to inject molten plastic and backward to replenish material.
Nozzle: Connects the barrel to the mold’s sprue or runner system.
Clamping Unit:
Platens: The stationary and movable plates that hold the mold halves securely.
Tie Bars: Strong bars that connect the platens and maintain the structural integrity of the machine.
Mold Clamp: The mechanism that provides the force to keep the mold closed during injection and cooling.
Mold:
Cavity: The hollow space in the mold where plastic takes its final shape.
Core: The component that shapes the internal features of the part.
Runner System: Channels that guide molten plastic from the nozzle to the mold cavities.
Sprue: The main channel through which plastic enters the runner system.
Cooling System:
Cooling Channels: Paths through the mold for circulating coolant (usually water) to rapidly cool and solidify the molten plastic.
Ejection System:
Ejector Pins: Push the part out of the mold after cooling.
Ejector Plate: A plate with pins that eject multiple parts simultaneously.
Hydraulic or Electric System:
Hydraulic Pump or Electric Motor: Provides power for mold clamping, ejection, and other functions.
Control System:
Human-Machine Interface (HMI): Touchscreen interface for setting and monitoring process parameters.
Programmable Logic Controller (PLC): Controls machine operations, adjusts parameters, and ensures safety.
Heating Elements:
Band Heaters: Wrap around the barrel to maintain the required temperature for melting plastic.
Sensors and Monitoring:
Thermocouples: Measure temperatures at various points in the machine and mold.
Pressure Transducers: Monitor injection pressure within the barrel and mold.
Position Sensors: Detect the position of moving parts like the mold or ejector.
Automation and Robotics:
Robots: Assist in tasks like part removal, placement, and quality inspection.
Material Handling:
Conveyors: Transport plastic pellets from storage to the hopper.
Dryers: Remove moisture from plastic pellets to maintain material quality.
Safety Features:
Emergency Stop Buttons: Instantly halt machine operations.
Safety Gates and Interlocks: Prevent access to hazardous areas while the machine is in operation.
These basic parts work together to execute the injection molding process and create plastic parts efficiently and accurately

My partner and I stumbled over here from a different web page and thought I should
check things out. I like what I see so now i am following you.
Look forward to exploring your web page repeatedly.
I like this post, enjoyed this one thankyou for posting.
Its good as your other posts : D, thanks for putting up. “There’s no Walter Cronkite to give you the final word each evening.” by William Weld.
Wohh just what I was searching for, thanks for putting up.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Having read this I thought it was very informative. I appreciate you taking the time and effort to put this article together. I once again find myself spending way to much time both reading and commenting. But so what, it was still worth it!