In the injection molding industry, molds are the heart of production. They define product quality, efficiency, and cost. A single mold breakdown can halt production, cause huge financial losses, and damage customer relationships. This is why Mold Preventive Maintenance (PM) is not just a technical practice but a critical business strategy.
A Mold Preventive Maintenance Check Sheet acts as a systematic tool to ensure that every inspection and service activity is carried out in a standardized manner. It is not just paperwork—it is a record of reliability, a communication bridge between production, tool room, and quality, and a proven method to extend mold life.
In this article, we will explore the structure, importance, and best practices of a Mold Preventive Maintenance Check Sheet. We will also cover Do’s and Don’ts, One Point Lessons (OPL), learning practices, and real feedback from operators and production departments. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive guide on how to design, use, and benefit from mold PM check sheets.

What is Mold Preventive Maintenance?
Mold Preventive Maintenance (PM) refers to scheduled inspections and servicing of molds to prevent unexpected breakdowns and maintain consistent production quality. Unlike breakdown maintenance, which only reacts to failures, preventive maintenance focuses on anticipating and solving problems before they disrupt production.
Types of maintenance in the molding industry include:
- Breakdown Maintenance: Fixing molds only when they fail. High downtime cost.
- Preventive Maintenance: Regular scheduled inspections, cleaning, lubrication, and repair to avoid failures.
- Predictive Maintenance: Using data (like shot count, sensors, or AI monitoring) to predict failures before they occur.
Among these, Preventive Maintenance is the most practical and cost-effective approach for small to mid-scale molding companies, and the check sheet is the backbone of this system.
Structure of a Mold Preventive Maintenance Check Sheet
A well-designed PM check sheet must be simple, clear, and standardized. It usually contains the following main sections:
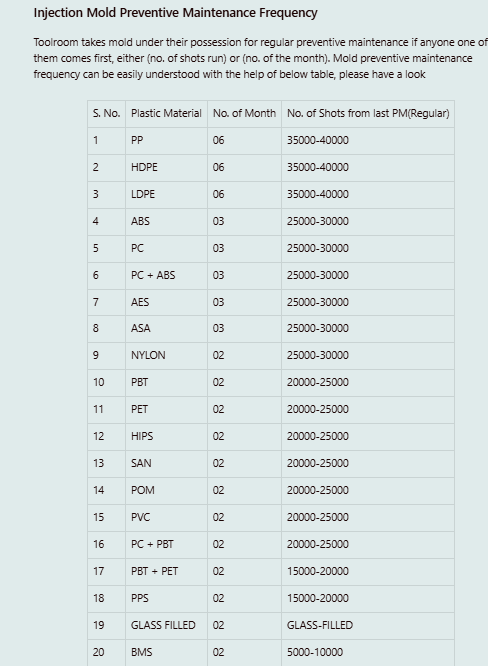
- Basic Mold Information
- Mold number, part number, customer, date, technician name.
- Cycle/shot count since last PM.
- Maintenance frequency (e.g., every 40,000 shots).
- Visual Inspection
- External damage, rust, cracks.
- Leaks from water/oil lines.
- Electrical and connector condition.
- Cavity and Core Inspection
- Surface scratches, rust, carbon deposits.
- Alignment, venting condition, wear marks.
- Ejection System
- Ejector pin condition and lubrication.
- Return pin movement.
- Guide pins, bushes, and slide wear.
- Cooling System
- Water channel blockage, scaling, rust.
- Hose and connector leak checks.
- Flow test verification.
- Hot Runner / Heating System (if applicable)
- Heaters, thermocouples, and wiring inspection.
- Manifold leak checks.
- Electrical continuity test.
- Lubrication & Cleaning
- Greasing moving parts.
- Cleaning vents and parting lines.
- Rust preventive oil application.
- Final Checks and Documentation
- Bolt tightening.
- Proper mold storage condition.
- Technician signature, remarks, and approvals.
- Feedback Section
- Inputs from production team.
- Operator observations during molding.
This structured approach ensures no critical point is missed.
Detailed Explanation of Mold Preventive Maintenance Checksheet
Basic Mold Information
This section creates traceability. By documenting mold ID, part name, and shot count, maintenance teams can monitor mold wear patterns and schedule PM more effectively. For example, some molds may require PM every 15,000 shots, while others may last 40,000 shots depending on material type.
Visual Inspection
Before deep inspection, a simple visual check can reveal obvious issues: rust on surface, oil or water leakage, damaged clamps. If ignored, these can lead to premature failures.
Cavity and Core Inspection
The cavity and core define part quality. Any scratch, rust, or misalignment directly reflects in defects such as flash, burn marks, or short shots. Proper vent cleaning prevents gas trapping, which is a major cause of black marks.
Ejection System
A sticky ejection system leads to broken parts, machine alarms, and downtime. Proper lubrication of ejector pins and slides is mandatory. Return pins must be checked for smooth functioning to avoid jamming.
Cooling System
Blocked cooling channels increase cycle time, reducing productivity. A 5-second increase in cycle time may seem small but, across 100,000 shots, it translates into thousands of lost parts. Scale removal and water flow testing are crucial.
Hot Runner / Heating System
In hot runner molds, heating elements and thermocouples are critical. A small wiring fault can lead to cold slug defects or full mold stoppage. Preventive inspection avoids sudden breakdowns.
Lubrication and Cleaning
Using proper grease is essential. Industrial-grade, mold-safe lubricants prevent wear without affecting molding material. Cleaning should be done with non-corrosive agents to protect cavities.
Final Checks and Documentation
Once all checks are complete, the mold should be stored properly with rust preventive coating. Documentation ensures accountability and traceability for audits and customer requirements.
Feedback Section
Production and machine operator feedback is often overlooked but is highly valuable. Operators notice real-time problems like ejector sticking, unusual sounds, or leaks during running. Capturing these inputs ensures preventive measures in the next PM cycle.
Do’s and Don’ts in Mold Preventive Maintenance
Do’s
- Follow PM frequency based on shot count and mold condition.
- Use approved lubricants and rust preventives.
- Document every inspection in the check sheet.
- Store molds in clean, dry conditions.
- Train technicians on handling sensitive mold parts.
Don’ts
- Don’t ignore minor leaks or cracks.
- Don’t store molds without applying rust preventive oil.
- Don’t mix spare parts (like ejector pins) between molds without record keeping.
- Don’t over-tighten bolts beyond torque specifications.
- Don’t clean cavities with hard brushes that can cause scratches.
One Point Lessons (OPL) in Mold Maintenance
One Point Lessons (OPL) are short, visual, one-page documents used to teach technicians simple, specific tasks.
Examples of OPL in mold maintenance:
- How to properly clean mold vents.
- Correct method of lubricating ejector pins.
- Safe mold lifting and handling practices.
Benefits:
- Quick training for new employees.
- Knowledge sharing within the team.
- Standardization of practices.
Learning and Continuous Improvement
PM check sheets are not static—they must evolve. By analyzing repeated issues recorded in the sheets, tool rooms can identify root causes and take corrective actions.
For example:
- If vent carbon buildup is recorded repeatedly → Improve molding temperature settings.
- If ejector pin wear is frequent → Change lubrication frequency or material.
This learning loop ensures continuous improvement in mold reliability.
Feedback from Production, Quality & Machine Operator Department
Take feedback from production/quality department & machine operator to work on mold for effective maintenance during mold maintenance, such as :
- Flashing at parting line.
- Burn marks.
- Short shots.
- Warpage due to cooling issues.
- Abnormal ejection sound.
- Water leakage during running.
- Difficulty in mold opening or closing.
Capturing this feedback in Mold Preventive Maintenance checksheets allows the tool room to focus on specific problem areas during preventive maintenance.
Integration with Quality and Audit Systems
Standards like IATF 16949 and customer audits (e.g., MSIL, OEM audits) demand evidence of tool maintenance. PM check sheets provide this traceability.
Benefits:
- Proof of preventive actions during audits.
- Easy root cause analysis with historical data.
- Better alignment with 7QC tools like Pareto charts and Cause-Effect analysis.
Digital Transformation of Mold Preventive Maintenance CheckSheet
Many companies are shifting from paper-based checklists to digital systems:
- Mobile/tablet-based inspection apps.
- Integration with ERP/MES for auto reminders.
- Data analytics to track mold performance.
This reduces human error and improves data visibility.
Conclusion
A Mold Preventive Maintenance Check Sheet is more than a checklist—it is a quality assurance tool, a cost-saving strategy, and a productivity booster. By combining structured check sheets, one point lessons, and continuous feedback, companies can extend mold life, improve product quality, and achieve customer satisfaction.
Investing in preventive maintenance is investing in the future reliability of your molding operations.
FAQs
Q1. What is the ideal frequency for mold preventive maintenance?
It depends on mold type, part design, and material. Typically, PM is scheduled every 15,000–40,000 shots.
Q2. What happens if Mold Preventive Maintenance checksheets are ignored?
Ignoring PM leads to unexpected breakdowns, higher repair costs, increased cycle time, and customer complaints due to poor part quality.
Q3. Who should fill the mold Preventive Maintenance checksheet?
Generally, tool room technicians or maintenance engineers fill mold preventive maintenance checksheet but feedback sections should involve production and operators.
Q4. Can a mold Preventive Maintenance checksheet be customized?
Yes. Every company should design the sheet based on their mold types (conventional, hot runner) and production conditions.
Q5. Is digital PM better than paper PM?
Yes. Digital PM systems improve traceability, reduce errors, and allow real-time monitoring, but small companies can still benefit from well-structured paper sheets.


Excellent breakdown, I completely agree with the challenges you described. For our projects we started using an AI-driven system called AI link building by OptiLinkAI, and it has simplified the entire process. It’s refreshing to see technology finally making link acquisition smarter, not just faster.
I am constantly thought about this, thankyou for putting up.
Wonderful site you have here but I was wondering if you knew of any community forums that cover the same topics talked about in this article? I’d really like to be a part of group where I can get comments from other experienced people that share the same interest. If you have any suggestions, please let me know. Kudos!
Wohh just what I was searching for, thanks for posting.
I like the helpful information you provide in your articles. I’ll bookmark your weblog and check again here regularly. I am quite certain I’ll learn a lot of new stuff right here! Best of luck for the next!