Thermoplastic materials are a class of polymers known for their versatility, wide-ranging properties, and broad applications across various industries. Unlike thermosetting plastics, which undergo irreversible chemical changes upon curing, thermoplastics can be melted and reshaped multiple times without undergoing significant chemical changes. This unique characteristic makes them invaluable in manufacturing processes. In this article, we will embark on a journey to explore thermoplastic materials, delving into their properties, processing methods, and diverse applications.

Understanding the Properties of Thermoplastic Materials
Thermoplastic materials exhibit a remarkable combination of properties that make them suitable for a multitude of applications. Some of the key characteristics include:
1. Flexibility and Durability
Thermoplastics are known for their flexibility, allowing them to be molded into various shapes and sizes. They can also endure repeated bending and stretching without breaking, making them ideal for products requiring resilience.
2. Melting and Re-Molding
One of the defining features of thermoplastics is their ability to soften and flow when heated, and then solidify when cooled. This property enables recycling and reshaping, reducing waste and production costs.
3. Chemical Resistance
Many thermoplastics are resistant to various chemicals, making them suitable for applications where exposure to corrosive substances is a concern.
4. Lightweight
Thermoplastics are generally lightweight, which is advantageous in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where weight reduction is crucial for fuel efficiency and performance.
5. Insulation Properties
Thermoplastic materials are excellent insulators of both heat and electricity, making them essential in electrical and electronic applications.
6. Transparency
Some thermoplastics, such as polycarbonate, offer high optical clarity, making them suitable for applications like eyewear lenses and display screens.
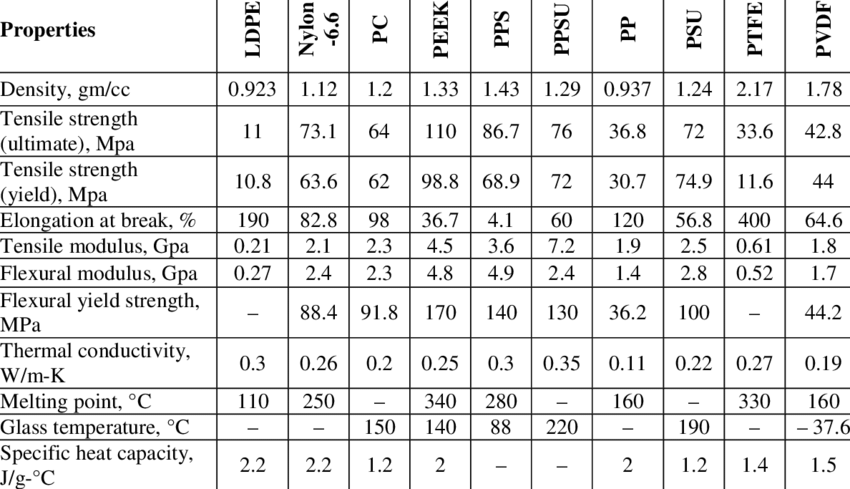
Thermoplastic Materials: Properties, Characteristics and Processing
Here’s a step-wise explanation of thermoplastic materials, covering their properties, characteristics, and processing –
1. Properties of Thermoplastic Materials
- Flexibility: Thermoplastics are known for their flexibility, allowing them to be molded into various shapes and sizes without breaking.
- Melting and Re-Molding: They can be melted and reshaped multiple times without undergoing chemical changes, making them recyclable.
- Chemical Resistance: Many thermoplastics resist chemicals, making them suitable for applications involving corrosive substances.
- Lightweight: They are generally lightweight and beneficial in industries like automotive and aerospace.
- Insulation: Excellent insulators of heat and electricity, thermoplastics are used in electrical and electronic applications.
- Transparency: Some, like polycarbonate, offer optical clarity, ideal for eyewear lenses and displays.
2. Characteristics of Thermoplastic Materials
- Reversibility: Thermoplastics can be melted and solidified repeatedly, unlike thermosetting plastics, which undergo irreversible chemical changes upon curing.
- Recyclability: Their ability to be re-molded and recycled reduces waste and production costs.
- Diverse Applications: Due to their versatility, thermoplastics find applications in various industries.
- Safety: Thermoplastic processing methods are generally safer as they don’t involve curing at high temperatures.
3. Processing Methods for Thermoplastic Materials
- Injection Molding: Melting the material and injecting it into a mold cavity to create products like packaging materials and automotive components.
- Extrusion: Forcing molten material through a die to produce items like pipes and plastic sheets.
- Blow Molding: Creating hollow objects, such as bottles, by inflating a molten preform within a mold.
- Thermoforming: Softening a thermoplastic sheet, stretching it over a mold, and cooling to create products like packaging trays.
- 3D Printing: Building objects layer by layer based on a digital design, commonly used for prototypes and custom parts.
Thermoplastic materials are integral to modern manufacturing, offering a wide range of possibilities due to their properties, characteristics, and diverse processing methods.
Types of Thermoplastic Materials
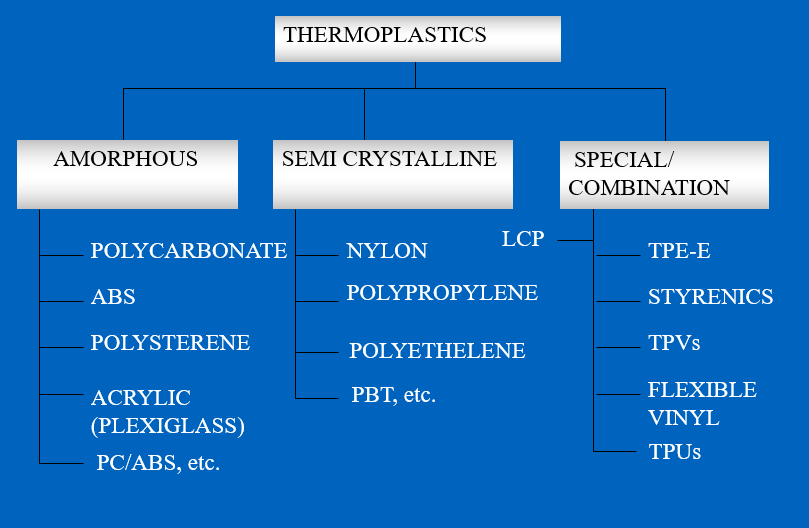
Here’s an explanation of different types of thermoplastic materials in a step-wise, concise manner –
- Type: PE includes various subtypes like HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) and LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene).
- Properties: PE is known for its lightweight, and chemical resistance, and is used in products ranging from plastic bags (LDPE) to water pipes (HDPE).
- Properties: PP offers high tensile strength, and chemical resistance, and is used in packaging, automotive components, and medical devices.
- Properties: PVC is known for its durability and is used in construction for pipes, window frames, and electrical insulation.
4. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
- Properties: PET is transparent, lightweight, and used in beverage bottles, textiles (polyester), and food packaging.
- Types: PS includes General-Purpose PS (GPPS) and High-Impact PS (HIPS).
- Properties: PS is lightweight, rigid, and used in packaging, disposable cutlery (HIPS), and insulation.
6. Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)
- Properties: PVDF offers excellent chemical resistance and is used in chemical processing, electrical wiring, and aerospace applications.
7. Polycarbonate (PC)
- Properties: PC is transparent, impact-resistant, and used in eyewear lenses, CDs/DVDs, and aircraft windows.
8. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
- Properties: ABS combines toughness with rigidity and is used in automotive parts, toys, and electronics.
9. Polyamide (Nylon)
- Types: Nylon 6, Nylon 66, and others.
- Properties: Nylon offers high strength, and durability, and is used in textiles, automotive components, and industrial applications.
10. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
- Properties: PMMA is transparent, lightweight, and used in products like acrylic glass, signage, and medical implants.
Processing Methods for Thermoplastic Materials
The versatility of thermoplastics extends to the various processing methods used to shape and manufacture products. Here are some common techniques –
1. Injection Molding
Injection molding is the most widely used method for thermoplastic processing. It involves melting the thermoplastic material and injecting it into a mold cavity. Once cooled, the material solidifies and takes the shape of the mold. This method is used to produce a wide range of products, from packaging materials to automotive components.

2. Extrusion
Extrusion involves forcing molten thermoplastic material through a die to create a continuous profile or shape. This process is commonly used to produce pipes, tubes, and plastic sheets.

3. Blow Molding
Blow molding is employed to create hollow, three-dimensional objects, such as bottles and containers. The process involves inflating a molten thermoplastic preform within a mold cavity until it takes the desired shape.

4. Thermoforming
Thermoforming utilizes heat to soften a thermoplastic sheet, which is then stretched over or into a mold and allowed to cool. This method is used to create items like packaging trays and consumer goods.

5. 3D Printing
With advancements in technology, 3D printing has become a popular method for producing prototypes and custom parts from thermoplastic materials. This additive manufacturing process builds objects layer by layer based on a digital design.
Applications of Thermoplastic Materials
Thermoplastic materials find applications in a wide array of industries, owing to their versatility and advantageous properties. Here are some notable examples –
1. Automotive Industry
Thermoplastics are used extensively in the automotive sector for components such as bumpers, interior panels, and lightweight structural parts. Their high impact resistance and low weight contribute to improved fuel efficiency.
2. Medical Devices
In the medical field, thermoplastics are utilized to manufacture devices like syringes, IV bags, and surgical instruments. Their biocompatibility and ease of sterilization make them ideal for healthcare applications.
3. Consumer Goods
From household items like containers and toys to electronic device casings and kitchenware, thermoplastic materials are omnipresent in our daily lives.
4. Aerospace
Thermoplastics are gaining popularity in aerospace applications due to their lightweight properties. They are used in aircraft interiors, structural components, and insulating materials.
5. Electrical and Electronics
Thermoplastic materials are essential in the production of electrical cables, connectors, and insulators due to their excellent electrical insulation properties.
6. Packaging
Packaging materials such as bottles, containers, and films are often made from thermoplastics due to their durability, versatility, and ability to protect products from external factors.
Conclusion
Thermoplastic materials have become the backbone of modern manufacturing, thanks to their unique combination of properties, adaptability in various processing methods, and wide-ranging applications. As technology continues to advance, the development of new thermoplastic materials and processing techniques is poised to revolutionize industries even further. With sustainability becoming increasingly important, the recyclability of thermoplastics adds to their allure, making them a driving force in the ever-evolving world of materials science and manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are thermoplastic materials?
Thermoplastic materials are a class of polymers that can be melted and reshaped multiple times without undergoing significant chemical changes.
What distinguishes thermoplastics from thermosetting plastics?
Thermoplastics can be melted and remolded, while thermosetting plastics undergo irreversible chemical changes upon curing.
What are some common properties of thermoplastics?
Common properties include flexibility, recyclability, chemical resistance, lightweight, and insulation.
How are thermoplastics processed into products?
Thermoplastics are processed using methods like injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, and thermoforming.
Can thermoplastic materials be recycled?
Yes, thermoplastics are recyclable due to their ability to be melted and re-molded.
What are the main types of thermoplastic materials?
HDPE, LDPE, PP, PVC, PET, PS, PVDF, PC, ABS, PMMA & many more are types of thermoplastic materials.
What is the significance of thermoplastic’s melting point?
The melting point determines the temperature at which a thermoplastic becomes pliable for processing.
Are thermoplastics biodegradable?
Some thermoplastics are biodegradable, while others are not. Examples of biodegradable thermoplastics include PLA (polylactic acid).
What are the applications of polyethylene (PE)?
PE is used in products like plastic bags (LDPE) and water pipes (HDPE).
What is the primary application of polyvinyl chloride (PVC)?
PVC is commonly used in construction for pipes, window frames, and electrical insulation.
Which thermoplastic material is transparent and used in eyewear lenses?
Polycarbonate (PC) is known for its transparency and impact resistance, making it ideal for eyewear lenses.
Can thermoplastic materials withstand exposure to chemicals?
Many thermoplastics, such as PVC and PVDF, are resistant to various chemicals.
Are thermoplastics used in the automotive industry?
Yes, thermoplastics are widely used in the automotive sector for components like bumpers and interior panels.
How do thermoplastics perform in electrical applications?
Thermoplastics are excellent insulators, making them suitable for electrical cables, connectors, and insulators.
Are there thermoplastics suitable for high-temperature applications?
Yes, thermoplastics like polyetheretherketone (PEEK) and polyimide (PI) can withstand high temperatures.
Can thermoplastics be colored or tinted?
Yes, thermoplastics can be easily pigmented to achieve various colors and tints.
Are there any environmentally friendly thermoplastics available?
Biodegradable thermoplastics like PLA are considered more environmentally friendly.

you could have an incredible blog right here! would you wish to make some invite posts on my weblog?
F*ckin’ awesome things here. I am very glad to see your article. Thanks a lot and i am looking forward to contact you. Will you please drop me a mail?
I’m impressed, I need to say. Really rarely do I encounter a weblog that’s both educative and entertaining, and let me let you know, you have got hit the nail on the head. Your thought is outstanding; the problem is one thing that not sufficient people are speaking intelligently about. I am very joyful that I stumbled throughout this in my seek for something relating to this.
Thanks so much for your appreciation
Terrific work! This is the type of info that are meant to be shared across the net. Disgrace on the seek engines for not positioning this post upper! Come on over and seek advice from my web site . Thank you =)
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Outstanding feature
This web site is my inspiration , real good design and style and perfect written content.