Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) is a ubiquitous and versatile polymer that touches our lives in numerous ways, from the bottles we drink to the fibers in our clothing. Understanding PET’s journey, from its raw materials to the end products we encounter daily, provides insights into the world of plastics and their impact on modern society. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of PET’s production, properties, processing methods, and wide-ranging applications, while also addressing its environmental considerations.
Raw Materials of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
The journey of PET begins with its raw materials, which are derived from petrochemical sources –
Terephthalic Acid (PTA)
This is a crucial precursor in PET production. PTA is synthesized from petroleum-based feedstocks through a series of chemical reactions.
Ethylene Glycol (EG)
Another essential component of PET, EG, is produced through the hydration of ethylene, which is obtained from natural gas or crude oil.
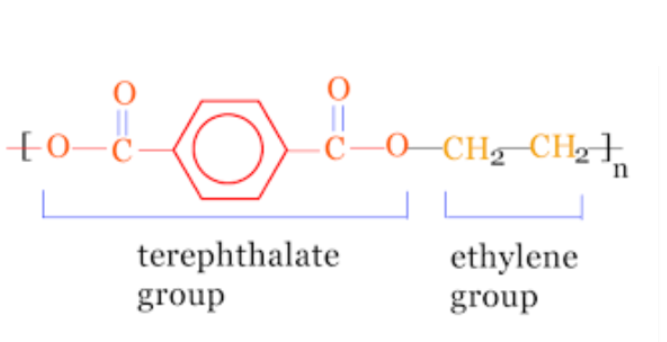
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Polymerization Process
The heart of PET’s journey lies in the polymerization process, where the raw materials are transformed into the polymer we know –
Esterification
Terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol are combined in a reactor, initiating an esterification reaction. This reaction forms dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) and monoethylene glycol (MEG) as intermediates.
Polycondensation
DMT and MEG are then subjected to polycondensation, a high-temperature and vacuum-based process that removes methanol and water, forming long chains of PET molecules. The result is a resin that can be further processed.
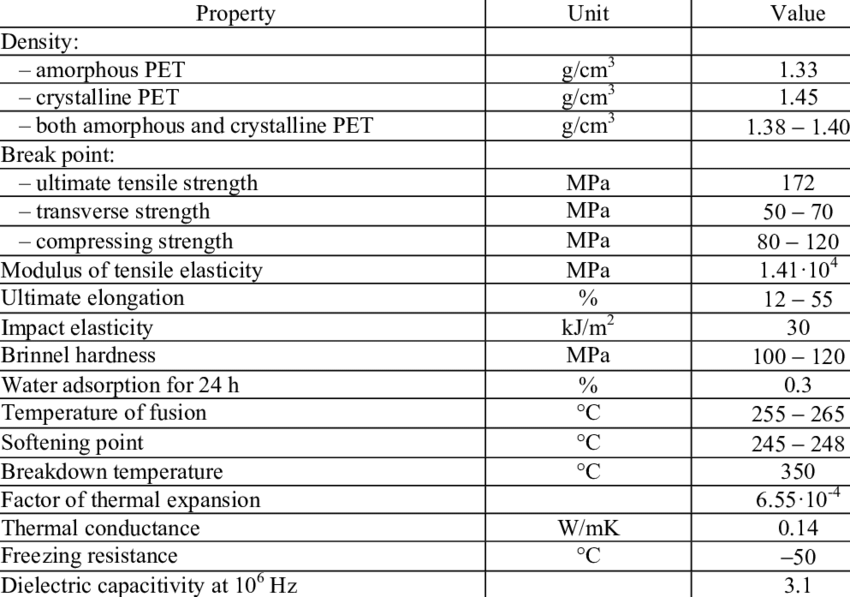
Properties and Characteristics of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Understanding the properties and characteristics of PET is key to comprehending its versatility and widespread use –
- High Strength and Durability: PET exhibits exceptional tensile strength, making it resilient and resistant to breakage. This property is crucial in various applications, such as bottles and industrial materials.
- Transparency and Clarity: PET’s optical properties make it an ideal choice for clear packaging materials like water bottles and food containers. It allows consumers to see the contents and assess quality easily.
- Chemical Resistance: PET is resistant to a broad spectrum of chemicals, including acids, bases, and alcohols, ensuring that it maintains its integrity when used for various purposes.
- Barrier Properties: PET offers excellent barrier properties against moisture, gases, and odors, essential for preserving the quality and shelf life of packaged goods.
- Lightweight: PET’s lightweight nature reduces transportation costs and minimizes its carbon footprint. This property is particularly advantageous in the packaging industry.
- Recyclability: PET is highly recyclable, making it a sustainable choice for many applications. It can be melted down and reused in various products, contributing to a circular economy.
Processing Methods of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
PET can be shaped into a wide range of products through various processing methods –
- Melt Spinning: This process involves melting the PET resin and extruding it through tiny holes to create long, continuous filaments. These filaments can be stretched to align the polymer chains, increasing their strength and crystallinity. This technique is commonly used in textile manufacturing.
- Blow Molding: For PET bottle production, the polymer is melted and then blown into a mold to create the desired shape. This method allows for the mass production of bottles with consistent quality.
- Injection Molding: PET can also be injection molded to produce various products, from automotive parts to packaging containers. This process entails melting the PET resin and injecting it into a mold cavity under high pressure.
- Extrusion: PET sheets can be produced through extrusion, which involves melting the polymer and forcing it through a die to create sheets of various thicknesses. These sheets are used in thermoforming processes to create packaging trays and containers.
Applications of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
The versatility of PET is reflected in its extensive range of applications –
- Packaging: PET is a cornerstone of the packaging industry, used for bottles, jars, and containers for beverages, food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. Its clarity, strength, and barrier properties make it an ideal choice for preserving and presenting products.
- Textiles: PET is transformed into polyester fibers, widely used in clothing, upholstery, carpets, and other textile products. These fibers are known for their durability and wrinkle resistance.
- Engineering Plastics: PET is used to manufacture engineering plastics, which find applications in automotive components, electrical insulators, and industrial machinery parts due to their high strength and durability.
- Films and Sheets: PET films and sheets are used for various purposes, such as packaging films, labels, and protective sheets for electronic devices.
- Medical Devices: Due to its biocompatibility and chemical resistance, PET is used in the medical field for producing surgical sutures, medical tubing, and other critical devices.
- 3D Printing: PET’s excellent printability and durability make it increasingly popular in the field of 3D printing.

Environmental Considerations for Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
While PET offers numerous advantages, it’s essential to address its environmental impact –
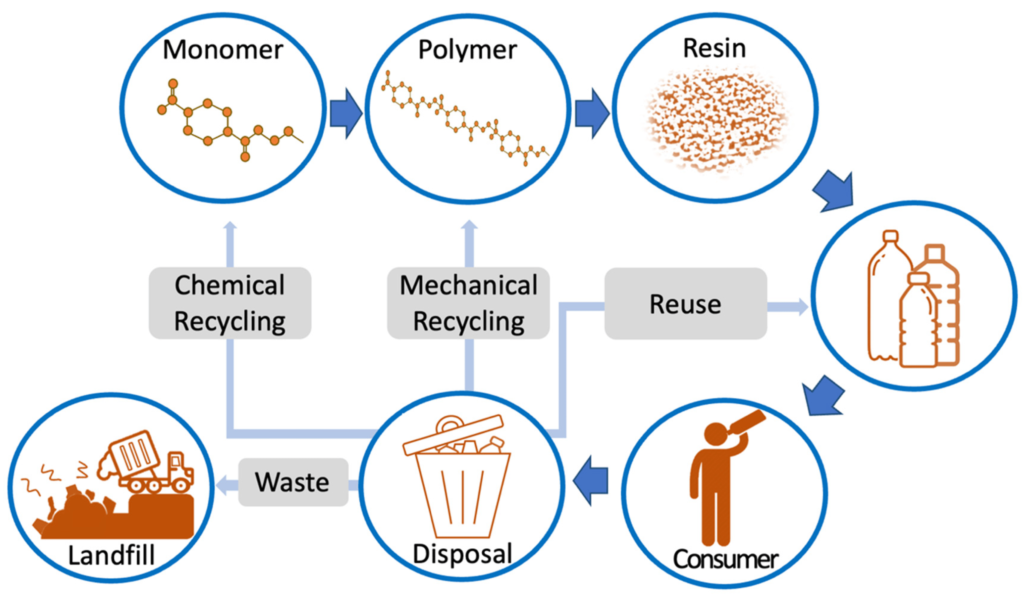
- Recycling: PET’s recyclability is a critical aspect of its environmental journey. PET bottles and containers can be recycled into new PET products, reducing the consumption of virgin materials and minimizing waste.
- Sustainability: Efforts are being made to develop alternative, bio-based sources for PET production. This shift toward renewable feedstocks can further reduce PET’s environmental footprint.
- End-of-Life Management: Proper disposal and recycling of PET products are essential to prevent environmental pollution. Education and infrastructure for recycling are key components of responsible PET use.

Conclusion
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) has come a long way from its raw materials to become an integral part of our daily lives. Its unique properties, diverse processing methods, and extensive applications demonstrate its importance in modern industry and consumer goods. While PET offers numerous advantages, it’s crucial to address its environmental impact through recycling and sustainable practices. Understanding PET’s journey highlights the complex interplay between science, technology, and sustainability in the world of plastics, ultimately shaping our future relationship with this versatile polymer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the advantages of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) over other plastics?
PET offers advantages such as clarity and transparency, high strength, excellent chemical resistance, and recyclability. Its lightweight nature also reduces transportation costs and environmental impact.
How can I identify Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) products for recycling purposes?
Most PET products are labeled with a recycling code “1” inside a triangle of arrows, which indicates that they are made of PET and are recyclable. However, it’s essential to check local recycling guidelines for specific instructions.
Can Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) be used for food packaging? Is it safe?
Yes, PET is commonly used for food and beverage packaging due to its excellent barrier properties and chemical resistance. It is considered safe for such applications and is approved by regulatory agencies worldwide.
How is Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) produced from its raw materials?
PET is produced through a polymerization process involving terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol. These raw materials undergo esterification and polycondensation reactions, resulting in the formation of PET resin.
What are the common applications of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)?
PET has a wide range of applications, including beverage and food packaging, textile manufacturing (polyester fibers), engineering plastics, films and sheets, medical devices, and 3D printing.
What are the key properties of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)?
PET exhibits several important properties, including high strength and durability, transparency, chemical resistance, excellent barrier properties, lightweight nature, and recyclability.
Is Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) a recyclable material?
Yes, PET is highly recyclable. PET bottles and containers can be collected, cleaned, and processed into new PET products, contributing to a more sustainable and circular economy.

Hello,
I have a piece with small holes. These holes are blocked with PET. What substance dissolves PET in itself? do you have cleaning needles in different sizes? Needles that can clean the PAT from the holes. Please answer me.
– With the rise in production and consumption of PET products, is the disposal and recycling of this material being adequately managed to prevent environmental harm?
Hi, Neat post. There’s a problem with your site in internet explorer, would test this… IE still is the market leader and a large portion of people will miss your wonderful writing due to this problem.
Way cool! Some extremely valid points! I appreciate you penning this
write-up and the rest of the website is also very good.
In it something is. Now all is clear, I thank for the information.
I express gratitude for the help in this question.
Same a urbanization any
It cannot be!
This excellent phrase is necessary just by the way
What excellent interlocutors 🙂
А где логика?
Да делали
As the expert, I can assist. I was specially registered to participate in discussion.
It is more than word!
What i do not understood is in truth how you are not actually a lot more smartlyliked than you may be now You are very intelligent You realize therefore significantly in the case of this topic produced me individually imagine it from numerous numerous angles Its like men and women dont seem to be fascinated until it is one thing to do with Woman gaga Your own stuffs nice All the time care for it up
There is noticeably a bundle to learn about this. I assume you made certain nice factors in features also.
Hi! I know this is kinda off topic however I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in trading links or maybe guest authoring a blog post or vice-versa? My blog covers a lot of the same subjects as yours and I believe we could greatly benefit from each other. If you happen to be interested feel free to shoot me an email. I look forward to hearing from you! Awesome blog by the way!
Great insights
You really make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this topic to be actually something which I think I would never understand. It seems too complicated and very broad for me. I am looking forward for your next post, I’ll try to get the hang of it!
Insightful piece
As soon as I noticed this web site I went on reddit to share some of the love with them.
F*ckin¦ amazing things here. I am very happy to peer your post. Thanks so much and i’m taking a look ahead to touch you. Will you please drop me a mail?