Introduction
In the realm of modern industrial manufacturing, precision, efficiency, and quality are paramount. Achieving these goals often hinges on the ability to control forces with accuracy and reliability. One technological innovation that has significantly impacted this aspect of industrial processes is the use of nitrogen gas springs. These specialized devices have revolutionized various applications by offering enhanced force management, improved performance, and elevated product quality. In this article, we delve into the world of nitrogen gas springs, exploring their mechanisms, advantages, and their widespread impact across a spectrum of industrial sectors.
Understanding Nitrogen Gas Springs: A Brief Overview
Nitrogen gas springs, also known as nitrogen springs or gas struts, are mechanical components designed to provide controlled force in various applications. They utilize the compressibility of nitrogen gas to generate force and offer a dynamic solution for tasks that demand precise load control, consistent motion, and minimized vibrations. These springs typically consist of a pressure-tight cylinder filled with nitrogen gas, a piston, and an oil-filled chamber. The pressure of the gas inside the cylinder determines the spring’s force characteristics.
Working Principle of Nitrogen Gas Springs
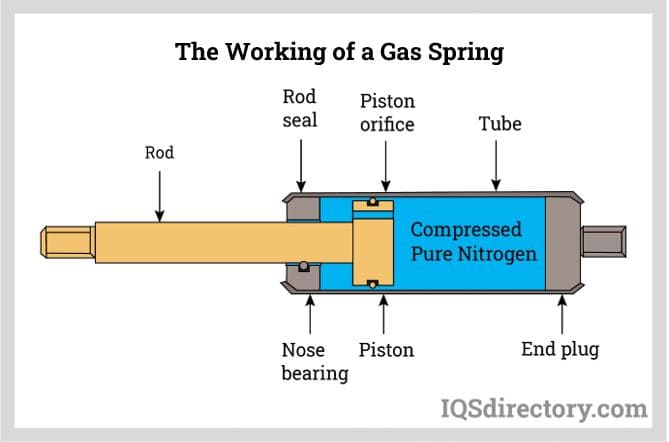
The working principle of nitrogen gas springs involves utilizing compressed nitrogen gas to generate controlled force and motion. By adjusting the gas pressure and piston configuration, these springs offer precise and repeatable force output, making them indispensable in applications that require accurate load management and controlled movement.
Here’s a step-wise explanation of how nitrogen gas springs function –
- Gas-Filled Cylinder:
- Nitrogen gas springs consist of a sealed cylinder filled with nitrogen gas under pressure.
- The gas is contained within the cylinder, creating a closed system.
- Piston and Oil Chamber:
- Inside the cylinder, there is a piston that separates the nitrogen gas from an oil-filled chamber.
- The piston is capable of moving within the cylinder.
- Gas Compression:
- When an external force is applied to the piston, it compresses the nitrogen gas in the cylinder.
- As the gas is compressible, it undergoes a reduction in volume, causing an increase in pressure within the cylinder.
- Force Generation:
- The compressed nitrogen gas exerts pressure on the piston, generating a force.
- This force is proportional to the pressure of the gas and the effective area of the piston.
- Controlled Motion:
- The generated force can be controlled by adjusting the gas pressure in the cylinder. Increasing the pressure increases the force output.
- The force generated can be used to compress, lift, or counteract external loads, depending on the application.
- Oil Damping:
- The presence of the oil-filled chamber serves multiple purposes.
- It acts as a damping mechanism, slowing down the motion of the piston to prevent rapid impacts or sudden movements.
- The damping effect enhances stability and reduces vibrations.
- Release and Expansion:
- When the external force is removed, the compressed nitrogen gas expands, pushing the piston back to its original position.
- As the gas expands, its pressure decreases, and the force output decreases accordingly.
- Force Adjustments:
- The force exerted by the nitrogen gas spring can be finely adjusted by modifying the gas pressure or the effective piston area.
- This adjustability allows for precise control over the generated force to match the application’s requirements.
- Applications:
- Nitrogen gas springs find applications in various industries, such as automotive, manufacturing, aerospace, robotics, and more.
- They are used for tasks like lifting, balancing, damping, and providing controlled motion in a wide range of industrial processes.
Components of Nitrogen Gas Springs
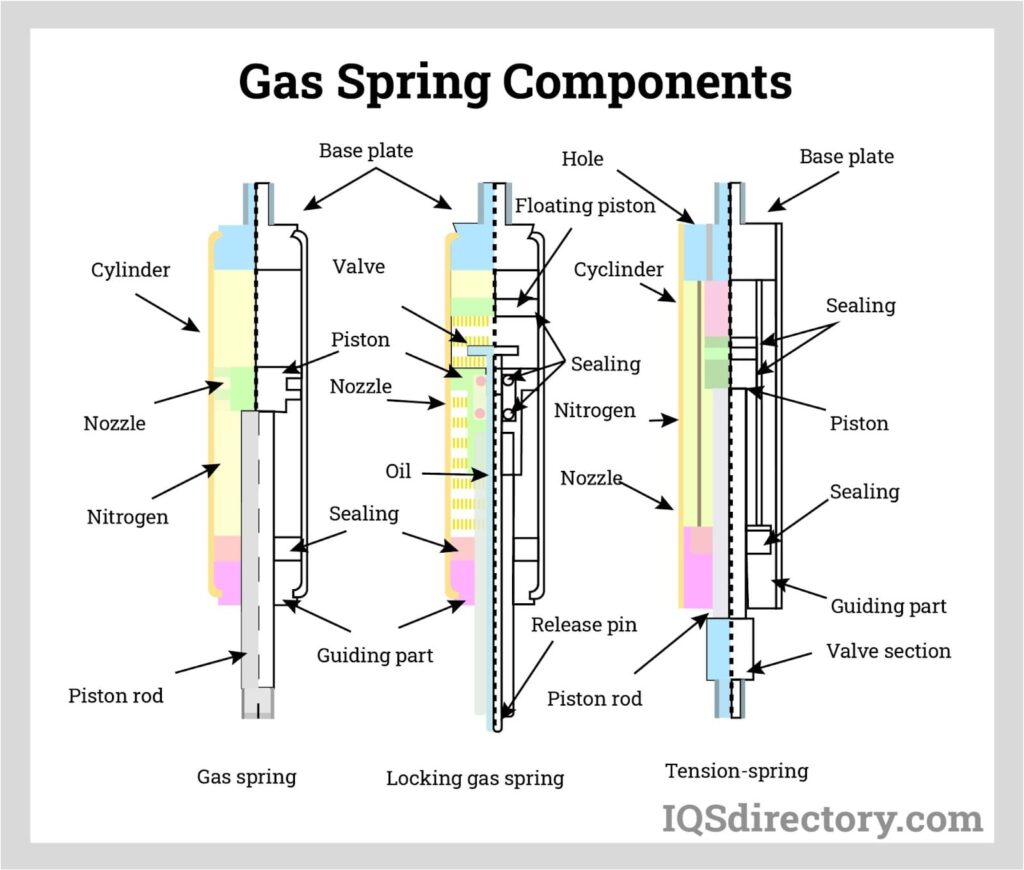
The components of a nitrogen gas spring are essential to its functioning, enabling the controlled generation of force and motion. Here’s a detailed step-wise breakdown of the components and their roles in a nitrogen gas spring –
1. Cylinder:
- The cylinder is a pressure-tight enclosure that contains the other components of the nitrogen gas spring.
- It holds the compressed nitrogen gas, creating a closed system that allows pressure buildup when the gas is compressed.
2. Piston:
- The piston is a movable component within the cylinder.
- It separates the nitrogen gas in the upper portion of the cylinder from the oil-filled chamber in the lower portion.
- The piston is responsible for transmitting the force generated by the compressed gas to the application.
3. Nitrogen Gas:
- Nitrogen gas is the primary medium used to generate force within the gas spring.
- It is initially present in the upper portion of the cylinder and becomes compressed when an external force is applied to the piston.
- The compressibility of the gas allows it to store energy and exert force when the gas spring is in use.
4. Oil-Filled Chamber:
- The lower portion of the cylinder is filled with oil.
- The oil-filled chamber serves several functions, including providing damping, lubrication, and a medium for transmitting force.
- When the piston moves, the oil flows between the piston and the cylinder walls, dampening the motion and preventing sudden impacts.
5. Seals and O-Rings:
- Seals and O-rings ensure airtight and pressure-tight sealing of the components.
- They prevent gas leakage and maintain the integrity of the closed system, ensuring consistent force output.
6. Valve System:
- Some nitrogen gas springs are equipped with valve systems that allow for adjustments to the gas pressure.
- The valve system enables fine-tuning of the force output by controlling the amount of nitrogen gas in the cylinder.
- By adjusting the gas pressure, the force characteristics of the gas spring can be customized for specific applications.
7. End Fittings:
- End fittings are components attached to the top and bottom of the cylinder.
- They provide mounting points for connecting the gas spring to the application and the support structure.
- End fittings vary in design, including threaded rods, eyelets, or other forms of connectors.
8. External Force:
- The external force applied to the piston initiates the compression of the nitrogen gas.
- This force can be manually applied or result from the weight or load of the machinery or component being controlled.
9. Expansion Mechanism:
- When the external force is removed, the compressed nitrogen gas expands, pushing the piston back to its original position.
- This expansion mechanism enables the gas spring to return to its neutral state, ready for the next cycle.
10. Materials and Construction:
- The components of a nitrogen gas spring are typically made from materials that offer durability, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with the nitrogen gas and oil used.
- Common materials include high-strength steel for the cylinder, piston, and end fittings, while the seals and O-rings may be made from elastomers.
In summary, a nitrogen gas spring’s components work in harmony to enable the controlled generation of force and motion. The interaction between the compressed nitrogen gas, the piston, the oil-filled chamber, and the other elements creates a dynamic system that provides precise force control, damping, and stability in a variety of industrial applications.
Breakdown Occurance & Their Troubleshooting in Nitrogen Gas Springs
Breakdowns in nitrogen gas springs can occur due to various factors, impacting their performance and functionality. Proper troubleshooting is essential to identify and address these issues promptly. Here’s a step-wise breakdown of potential breakdowns in nitrogen gas springs and their troubleshooting –
1. Loss of Force or Load Capacity:
- Symptoms: The gas spring doesn’t provide the expected force or support the required load.
- Possible Causes:
- Gas Leakage: Air or gas leaking from the cylinder.
- Reduced Gas Pressure: The gas pressure inside the cylinder is too low.
- Troubleshooting:
- Check for visible gas leaks around seals and connections.
- Test the force output and compare it to specifications.
- If gas pressure is low, refill or adjust as per manufacturer guidelines.
2. Uneven Force Output:
- Symptoms: The force provided by the gas spring is inconsistent or varies during operation.
- Possible Causes:
- Uneven Gas Distribution: Gas is unevenly distributed within the cylinder.
- Piston Binding: Piston movement is hindered.
- Troubleshooting:
- Inspect the piston for any obstructions or damage.
- Confirm proper lubrication of the piston and seals.
- Consider purging the cylinder to ensure even gas distribution.
3. Noisy Operation:
- Symptoms: The gas spring produces unusual noises during compression or expansion.
- Possible Causes:
- Rapid Gas Expansion: Gas expansion occurs abruptly.
- Lack of Lubrication: Components experience friction without proper lubrication.
- Troubleshooting:
- Ensure proper lubrication of moving parts.
- Check if the noise is due to abrupt gas expansion.
- If the noise persists, inspect for damaged or worn components.
4. Slow or Delayed Return:
- Symptoms: The gas spring returns to its original position slowly or with a delay.
- Possible Causes:
- Oil Contamination: Oil-filled chamber is contaminated or deteriorated.
- Clogged Passages: Oil passages are obstructed.
- Troubleshooting:
- Inspect the oil-filled chamber for contamination or depletion.
- Verify that oil passages are clear and unobstructed.
- Replace oil if it’s degraded or contaminated.
5. Inconsistent Damping:
- Symptoms: The damping effect varies, leading to inconsistent motion control.
- Possible Causes:
- Inadequate Oil: Insufficient oil in the chamber.
- Varying Temperatures: Oil properties change with temperature fluctuations.
- Troubleshooting:
- Ensure the oil-filled chamber has the correct amount of oil.
- Choose an oil with suitable viscosity across operating temperatures.
- Monitor and adjust oil levels based on manufacturer recommendations.
6. Excessive Wear or Damage:
- Symptoms: Components show signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
- Possible Causes:
- Lack of Maintenance: Insufficient care and maintenance.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to harsh conditions or chemicals.
- Troubleshooting:
- Establish a regular maintenance schedule.
- Protect the gas spring from harsh environments and chemicals.
- Replace worn or damaged components as needed.
7. Valve Malfunctions:
- Symptoms: Valve adjustments don’t result in the expected force changes.
- Possible Causes:
- Valve Blockage: The valve system is obstructed or clogged.
- Valve Wear: Valve components are worn or damaged.
- Troubleshooting:
- Inspect the valve system for obstructions.
- Check for signs of wear in valve components.
- Clean or replace valves as necessary.
8. Corrosion and Rust:
- Symptoms: Visible corrosion or rust on external surfaces.
- Possible Causes:
- Exposure to Moisture: Prolonged exposure to humid or wet environments.
- Lack of Protective Coating: Absence of corrosion-resistant coatings.
- Troubleshooting:
- Apply appropriate coatings to protect against corrosion.
- Store and operate the gas springs in dry environments.
- If corrosion is severe, consider replacing affected parts.
Nitrogen Gas Springs Supplier

Here are the names of some nitrogen gas spring suppliers in India –
- Widder Springs India Pvt. Ltd.: A leading manufacturer of nitrogen gas springs, offering a wide range of products for various industrial applications.
- Aacess Equipments: They provide nitrogen gas springs for diverse industries, along with other industrial equipment.
- Ozone Springs Ltd.: Specializing in gas springs, they offer solutions for automotive, furniture, and industrial applications.
- Hydropack India Pvt. Ltd.: Supplier of nitrogen gas springs and hydraulic systems for industrial and automation needs.
- Star Springs Co.: Known for their range of gas springs, they cater to industries such as automotive, furniture, and medical equipment.
- Force Tech Engineers: They offer nitrogen gas springs and other industrial components for precision applications.
- Tooltech Global Engineering Pvt. Ltd.: Supplier of gas springs and related tooling components for manufacturing industries.
- Tech Spring Manufacturing Pvt. Ltd.: Providing nitrogen gas springs, mechanical springs, and various industrial solutions.
- Arrow Pneumatics & Hydraulics Pvt. Ltd.: Offering a range of industrial products including nitrogen gas springs.
- Canara Hydraulics Pvt. Ltd.: A supplier of hydraulic and pneumatic components, including nitrogen gas springs.
Here are the names of some nitrogen gas spring suppliers in the United States of America –
- Associated Spring Raymond: A leading manufacturer of nitrogen gas springs offering a wide range of products for various industrial applications.
- Hyson Products: Known for their precision nitrogen gas springs and hydraulic systems used in metal forming and other applications.
- DADCO, Inc.: Supplier of nitrogen gas springs and related components for the stamping and forming industry.
- Special Springs USA: Offers a variety of gas springs and related solutions for industrial and automotive applications.
- Darnell-Rose: Supplier of gas springs, dampers, and related products for industries like aerospace, automotive, and furniture.
- Bansbach Easylift of North America: Specializes in gas springs, dampers, and related motion control products for various sectors.
- Vektek, Inc.: Provides a range of work-holding solutions, including nitrogen gas springs, for industrial applications.
- Industrial Gas Springs, Inc.: Supplier of nitrogen gas springs for industrial, automotive, and aerospace applications.
- Isotech, Inc.: Offers a selection of gas springs and related products for automation and industrial applications.
- Optimum Spring Solutions: Provides nitrogen gas springs and various types of springs for industries like automotive, aerospace, and more.
When considering suppliers, it’s recommended to visit their websites, check their product offerings, and contact them directly to ensure they can meet your specific requirements and provide the necessary support for your projects.
Advantages Driving Adoption
The adoption of nitrogen gas springs has proliferated across numerous industrial sectors due to a host of distinct advantages they offer –
- Precise Force Control: Nitrogen gas springs allow for finely tuned force adjustment, ensuring that the desired force levels are achieved consistently. This precision is crucial in applications such as metal forming, die casting, and assembly processes.
- Consistency and Repeatability: These springs provide predictable and repeatable force characteristics, minimizing variability in production processes. This results in consistent product quality and reduced rejects.
- Vibration Damping: Nitrogen gas springs dampen vibrations and shocks, enhancing operational stability and protecting sensitive equipment or components during high-impact tasks.
- Increased Safety: The controlled force exerted by nitrogen gas springs enhances workplace safety by preventing sudden releases of energy and minimizing the risk of accidents.
- Reduced Maintenance: With fewer moving parts, nitrogen gas springs experience minimal wear and require less maintenance compared to traditional mechanical springs.
- Space Efficiency: Their compact design allows nitrogen gas springs to be integrated into space-restricted environments while delivering significant force output.
- Versatile Applications: From automotive manufacturing and aerospace assembly to robotics and packaging machinery, nitrogen gas springs find utility in a diverse range of industrial applications.
Applications Across Industries
The influence of nitrogen gas springs spans numerous sectors, each benefiting from their unique capabilities:
- Automotive Manufacturing: In automotive assembly lines, nitrogen gas springs assist in tasks such as door closure, seat adjustment, and hood positioning. Their precise force control ensures accurate fit and finish.
- Metal Stamping and Forming: Nitrogen gas springs have redefined metal forming processes by offering predictable force profiles for punching, bending, and deep drawing operations. This enhances both the quality and speed of production.
- Plastic Injection Molding: These springs play a pivotal role in plastic injection molding machinery, helping maintain consistent mold pressure for uniform product quality.
- Aerospace Engineering: In the aerospace industry, where precision is non-negotiable, nitrogen gas springs assist in delicate assembly processes, ensuring components fit together flawlessly.
- Robotics and Automation: Nitrogen gas springs dampen vibrations and provide controlled motion in robotic arms, enhancing accuracy during tasks like pick-and-place operations.
- Packaging and Material Handling: In packaging lines, nitrogen gas springs enable smooth and precise motion, ensuring packages are handled gently while maintaining efficiency.
The Future of Nitrogen Gas Springs
As industries continue to evolve and demand ever-increasing levels of precision and efficiency, the role of nitrogen gas springs is set to expand further. Advances in materials, design, and technology will likely lead to even more specialized applications and increased adoption across industries. Moreover, as sustainability and energy efficiency gain prominence, nitrogen gas springs’ ability to provide controlled force without wasteful energy dissipation becomes even more significant.
Conclusion
Nitrogen gas springs have emerged as indispensable tools for enhancing performance, quality, and safety in a multitude of industrial applications. Their ability to provide precise force control, dampen vibrations, and ensure consistency makes them a driving force behind modern manufacturing’s pursuit of excellence. As industries embrace their benefits, nitrogen gas springs are poised to shape the future of industrial processes, delivering on the promise of efficiency, precision, and innovation.
FAQ’s
Why Nitrogen Gas is used in Gas Springs?
Nitrogen gas is commonly used in gas springs due to its unique properties that make it suitable for providing controlled force and motion in various industrial applications. Here’s why nitrogen gas is used in gas springs –
1. Inertness: Nitrogen gas is chemically inert, which means it doesn’t readily react with other substances. This inertness prevents corrosion, oxidation, and other chemical reactions that could compromise the integrity of the gas spring’s components over time.
2. Compressibility: Nitrogen gas is highly compressible, allowing it to be easily compressed within the cylinder of the gas spring. This property enables the gas spring to store energy as the gas is compressed, which can then be released to generate controlled force and motion.
3. Consistency: Nitrogen gas exhibits consistent behavior within a specified pressure range. This predictability ensures that the force generated by the gas spring remains relatively constant over its operational life, providing reliability and accuracy in force applications.
4. Pressure Regulation: Nitrogen gas pressure can be precisely controlled by adjusting the amount of gas within the cylinder. This adjustability allows manufacturers to design gas springs with specific force characteristics to suit different applications.
5. Non-Flammable: Nitrogen gas is non-flammable and non-explosive, enhancing the safety of gas spring operation. This property is crucial in applications where sparks or open flames are present.
6. Inert Gas Properties: Nitrogen gas helps prevent moisture and contaminants from entering the gas spring’s internal components. This ensures consistent performance and minimizes the risk of gas contamination that could affect the spring’s behavior.
7. Thermal Stability: Nitrogen gas maintains its properties across a range of temperatures, making it suitable for applications with varying environmental conditions. Changes in temperature have minimal impact on the gas’s compressibility and pressure characteristics.
8. Environmentally Friendly: Nitrogen gas is abundant in the Earth’s atmosphere, making it an environmentally friendly choice for gas springs. It doesn’t contribute to ozone depletion or greenhouse gas emissions.
Due to these properties, nitrogen gas provides a stable, reliable, and controllable medium for generating force in gas springs. It allows for precise force adjustment, consistent performance, and safe operation across various industrial applications, from automotive and manufacturing to aerospace and robotics.
How to repair damaged Nitrogen Gas Springs?
Repairing damaged nitrogen gas springs can be a complex task and might not always be recommended, as gas springs are precision components that require specific knowledge and equipment. In many cases, it might be safer and more cost-effective to replace a damaged gas spring with a new one. However, if you’re considering repairing a gas spring, here are some general steps to follow –
1. Assessment:
Carefully inspect the gas spring to identify the extent of the damage. Look for signs of leakage, corrosion, wear, or deformation in the components.
2. Identify the Issue:
Determine the specific issue causing the damage. It could be gas leakage, piston binding, valve malfunction, or other factors.
3. Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and documentation for the gas spring model. They might provide recommendations for repairs or replacements.
4. Gas Spring Knowledge:
Gas springs are precision components with specialized seals, valves, and internal mechanisms. Attempting repairs without proper knowledge might lead to further damage or unsafe operation.
5. Professional Assistance:
If you’re not experienced in gas spring repair, consider seeking help from a professional who specializes in gas spring maintenance and repairs.
6. Replacement Parts:
If the damage is repairable and you have the necessary expertise, you might need replacement parts like seals, valves, or O-rings. Ensure these replacement parts are compatible with the gas spring model.
7. Tools and Equipment:
Gas spring repairs might require specific tools and equipment. These could include seal installation tools, pressure gauges, and specialized lubricants.
8. Safety Precautions:
Working with gas springs involves handling compressed gas and potential hazards. Follow safety guidelines, wear applicable defensive gear, and work in a well-ventilated area.
9. Testing:
After repairs, thoroughly test the gas spring’s functionality, force output, and damping. Ensure that the repaired gas spring meets the manufacturer’s specifications.
10. Consider Replacement:
If the damage is extensive or critical components are compromised, it might be safer and more cost-effective to replace the gas spring with a new one.
Remember that gas springs are precision-engineered components that play a crucial role in various applications. While minor maintenance might be possible, repairing damaged gas springs requires expertise and careful attention to detail. If in doubt, consult with professionals who have experience in gas spring repair and maintenance to ensure the safety and reliability of the repaired unit.
Explain the term Nitrogen Gas Springs Tester?

A Nitrogen Gas Springs Tester, also known as a Gas Spring Testing Machine, is a specialized equipment used to assess and evaluate the performance, characteristics, and properties of nitrogen gas springs.
These testers are designed to measure various parameters of gas springs, ensuring they meet quality standards, force specifications, and safety requirements. The primary purpose of a Nitrogen Gas Springs Tester is to ensure that gas springs function reliably and consistently within their intended applications. Here’s a closer look at the term –
Key Functions and Features:
Force Measurement: Gas spring testers measure the force output of the gas spring at various deflection points. This ensures that the force generated by the gas spring aligns with its intended specifications.
Compression and Extension Testing: The tester can simulate the compression and extension movements of the gas spring, allowing for evaluating its force output under different load and motion conditions.
Force-Deflection Characteristics: These testers help to generate force-deflection curves, providing insights into how the gas spring behaves across its operating range.
Durability Testing: Gas spring testers can subject the spring to repeated cycles of compression and extension, simulating real-world usage conditions to assess its long-term durability.
Damping Analysis: Some advanced testers can also evaluate the damping characteristics of the gas spring, assessing how well it absorbs shocks and vibrations during compression and extension.
Data Recording and Analysis: Testers often include data logging capabilities, allowing users to record force measurements, deflection values, and other relevant parameters for analysis.
Quality Assurance: Gas spring testers play a crucial role in quality control, ensuring that manufactured gas springs meet predetermined standards and specifications before they are integrated into industrial applications.
Benefits:
Precision: Gas spring testers provide accurate and repeatable force measurements, ensuring consistent quality across a batch of gas springs.
Performance Validation: Testers help manufacturers validate that gas springs perform as expected, reducing the risk of faulty products reaching the market.
Efficiency: These testers streamline the testing process, allowing for rapid evaluation of multiple gas springs in a shorter time frame.
Safety: By ensuring that gas springs meet safety and performance requirements, testers contribute to the safe operation of equipment and machinery that relies on gas springs.
Data-Driven Decisions: The data generated by gas spring testers provide valuable insights into the behavior of gas springs, enabling manufacturers to make informed design and production decisions.

Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.