In this article, you will learn about injection molding raw materials, their types, properties, applications, products, etc. Read the full article to learn more about plastic raw materials.
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced and interconnected world, the demand for plastic products has reached unprecedented heights, making plastics one of the most widely used materials across various industries. As a result, the plastic raw material market has become a dynamic and critical aspect of modern global trade. For purchasers and procurement professionals, understanding the intricacies of this market is paramount to ensure the smooth functioning of supply chains and the success of their businesses.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into various types of injection molding materials, explore their properties, and examine their applications in different industries. Whether you are a product designer, engineer, or industry professional, understanding these materials is crucial for achieving optimal results in your injection molding projects.

What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing process in which molten material is injected under high pressure into a mold cavity, causing it to cool and solidify, eventually forming the desired product. It is one of the most widely used methods for the production of large-scale plastic parts due to its high efficiency, repeatability, and ability to create complex shapes.
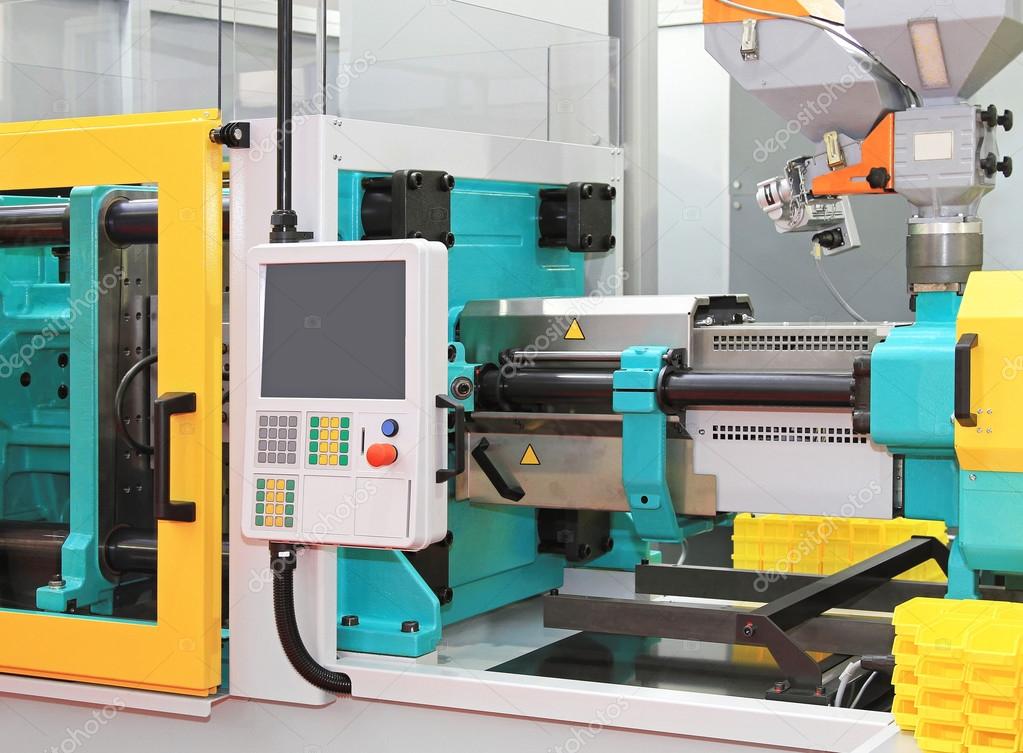

Types of Injection Molding Materials
1. Thermoplastics
Thermoplastics are the most commonly used materials in injection molding. They have unique properties that make them ideal for various applications. The most widely utilized thermoplastics for injection molding are –

A. Polyethylene (PE)
- Properties: High flexibility, chemical resistance, and low cost.
- Applications: Packaging, containers, and toys.

B. Polypropylene (PP)
- Properties: Excellent chemical resistance, lightweight, and high impact strength.
- Applications: Automotive parts, medical devices, and food containers.

C. Polystyrene (PS)
- Properties: Good electrical insulation, low density, and transparent options available.
- Applications: Disposable cutlery, CD cases, and electronic housings.

D. Polycarbonate (PC)
- Properties: High impact resistance, optical clarity, and excellent dimensional stability.
- Applications: Eyewear lenses, automotive headlamps, and electronic components.

E. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
- Properties: High toughness, good heat resistance, and easy to process.
- Applications: Consumer electronics, automotive interior parts, and sporting equipment.
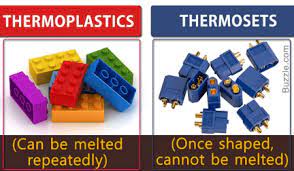
2. Thermosetting Plastics
Unlike thermoplastics, thermosetting plastics undergo irreversible chemical changes when heated and molded, resulting in a hardened and durable final product. Common thermosetting plastics used in injection molding include –
A. Phenolic Resin
- Properties: High heat resistance, excellent electrical insulator, and low cost.
- Applications: Circuit breakers, electrical sockets, and appliance handles.

B. Urea Formaldehyde (UF)
- Properties: Good scratch resistance, high tensile strength, and dimensional stability.
- Applications: Buttons, electrical switches, and household articles.
C. Epoxy Resin
- Properties: Superior chemical resistance, and exceptional adhesive properties.
- Applications: Adhesives, coatings, and electrical potting compounds.
Properties of Injection Molding Materials
The success of any injection molding project depends on understanding the properties of the chosen materials. Some key properties to consider include –
1. Mechanical Properties
- Tensile strength: The material’s ability to withstand pulling forces.
- Flexural strength: The ability to resist deformation under bending.
- Impact strength: The ability to absorb energy without fracturing.
- Hardness: The material’s resistance to indentation.
2. Thermal Properties
- Melting point: The temperature at which the plastic raw material changes into liquid from solid.
- Heat deflection temperature: The temperature at which the material deforms under load.
3. Chemical Resistance
- The ability of the material to resist chemical reactions or degradation when exposed to various substances.
4. Electrical Properties
- Dielectric strength: The material’s ability to resist electric breakdown.
- Volume resistivity: The material’s resistance to the flow of electrical current.
5. Optical Properties
- Transparency: The degree to which light passes through the material.
Applications of Injection Molding Materials
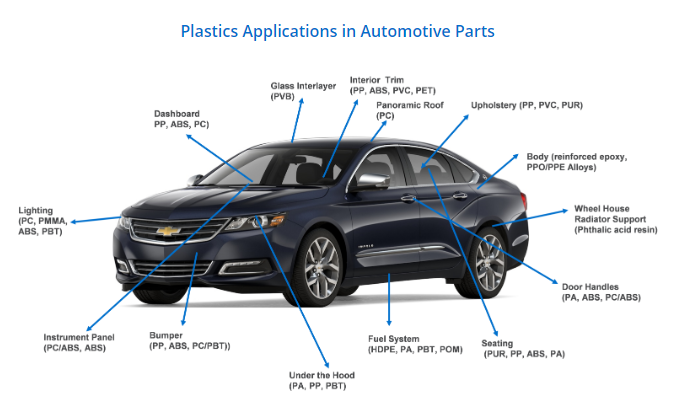
1. Automotive Industry
- Using injection molding materials for manufacturing automotive parts, such as bumpers, dashboards, and interior trims.
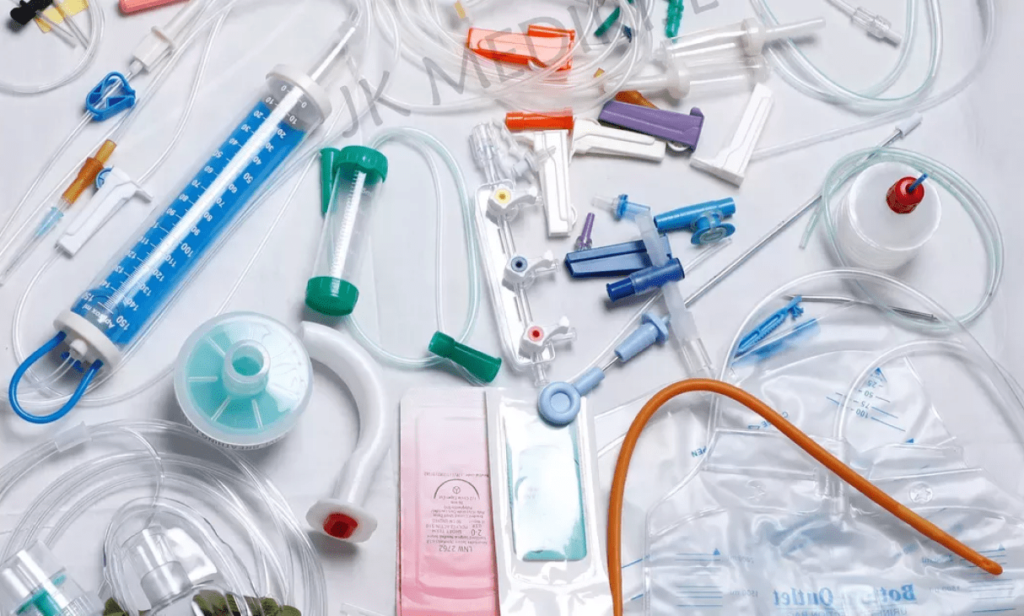
2. Medical Industry
- Medical devices, such as syringes, IV components, and surgical instruments, are commonly manufactured using injection molding materials.
3. Consumer Electronics
- Injection molding materials play a crucial role in producing casings, connectors, and other components for smartphones, laptops, and other electronic devices.

4. Packaging
- Injection molding materials are widely used to produce various packaging items, including bottles, caps, and containers.
5. Aerospace
- The aerospace industry relies on injection molding materials to manufacture lightweight, durable components for aircraft and spacecraft.
Pros and Cons of Injection Molding Materials
Injection molding machines are essential tools in the manufacturing industry, used to produce a wide range of plastic products and components. As with any technology, they come with their set of advantages and disadvantages. Let’s examine the pros and cons of injection molding machines –
1. Pros
A. High Efficiency
Injection molding machines can mass-produce identical parts with high precision and speed. The automated process allows for rapid and continuous production, reducing cycle times and increasing overall efficiency.
B. Versatility
These machines can produce complex and intricate shapes with ease. They offer a wide range of design possibilities, making them suitable for various industries, including automotive, electronics, medical, and consumer goods.
C. Material Selection
Injection molding supports a vast array of thermoplastic and thermosetting materials, offering manufacturers flexibility in material selection. This enables them to choose materials with specific properties, such as strength, flexibility, or heat resistance, to meet the product’s requirements.
D. Minimal Material Waste
Injection molding minimizes material wastage, as the excess material can be collected and recycled for future use. This efficiency contributes to cost-effectiveness and sustainability.
E. Low Labor Costs
Once the machine is set up and programmed, the injection molding process requires minimal human intervention. This reduces labor costs, especially in high-volume production scenarios.
2. Cons
A. High Initial Investment
The cost of acquiring and setting up an injection molding machine can be substantial, especially for small businesses or startups. The expense includes the machine itself, molds, and auxiliary equipment.
B. Complex Design and Tooling
The design and manufacturing of molds can be intricate and time-consuming. Complex parts may require specialized molds, increasing the overall production lead time and cost.
C. Material Constraints
While injection molding offers a wide material selection, not all materials are suitable for the process. Some high-temperature or chemically reactive materials may pose challenges or require specialized equipment.
D. Design Limitations
Certain designs may be challenging to mold, leading to limitations on part geometry and thickness. Sharp corners, thin walls, or undercuts may require additional considerations during the design phase.
E. Environmental Impact
The injection molding process relies on petroleum-based plastics, which can have significant environmental consequences. While recycling helps mitigate waste, it may not eliminate all environmental concerns associated with plastic usage.
Conclusion
Choosing the right injection molding materials is essential for achieving successful and efficient manufacturing processes. Each type of material possesses unique properties that cater to specific applications and industries. By understanding the properties and applications of various injection molding materials, designers and engineers can make informed decisions to produce high-quality plastic parts that meet the demands of modern industries. Whether it’s for the automotive, medical, consumer electronics, packaging, or aerospace sector, injection molding materials continue to revolutionize the way we manufacture and use plastic products.
The most frequently asked question I took from Google search and tried to answer some questions –
What is the definition of injection molding materials?
Injection molding materials refer to the various types of thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics used in the injection molding process, where molten material is injected into a mold to produce plastic parts with precision and efficiency.
What material is used for injection molding?
Thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics are commonly used for injection molding, as they can be melted and shaped into complex parts during the process.
What is the injection molding process?
The injection molding process involves injecting molten material, typically thermoplastics or thermosetting plastics, into a mold cavity under high pressure. The material cools and solidifies, allowing the creation of precise and complex plastic parts for various industries.
What is material injection?
Material injection is a manufacturing process where molten material, often thermoplastics or thermosetting plastics, is forced into a mold under high pressure. This process allows for the creation of intricate and durable plastic components used in various industries.
What are injection mold steel materials?
Injection mold steel materials are specialized alloys with high hardness, wear resistance, and thermal conductivity, designed for use in injection molding processes. Common types include P20, H13, and S136. These steels withstand the stress and high temperatures of molding, ensuring long-lasting molds capable of producing high-quality plastic parts with precise details and minimal defects.


I like this site it’s a master piece! Glad I found this
I love meeting utile info, this post has got me even more info! .
Your place is valueble for me. Thanks!…
Hello. impressive job. I did not imagine this. This is a splendid story. Thanks!
Its such as you learn my thoughts! You appear to understand so much about this, such as you wrote the guide in it or something. I think that you simply can do with a few to power the message house a bit, but other than that, this is excellent blog. An excellent read. I’ll certainly be back.
But wanna comment on few general things, The website style and design is perfect, the content material is really great. “To establish oneself in the world, one has to do all one can to appear established.” by Francois de La Rochefoucauld.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Very interesting topic, thankyou for putting up. “All human beings should try to learn before they die what they are running from, and to, and why.” by James Thurber.
Loved this piece
Im no longer certain the place you are getting your info, but good topic. I needs to spend some time learning much more or understanding more. Thank you for excellent information I used to be in search of this information for my mission.
Attractive component to content. I just stumbled upon your blog and in accession capital to say that I get in fact loved account your weblog posts. Anyway I’ll be subscribing on your feeds and even I fulfillment you get entry to persistently fast.