Overview
In the dynamic world of manufacturing, where innovation drives progress, new product development (NPD) is a pivotal process. NPD involves conceiving, designing, and bringing novel products to the market. Among the various industries that engage in NPD, the plastic parts development sector is prominent due to its vast applications in automotive, consumer goods, electronics, medical devices, and more. This article delves into the challenges plastic parts developers face during the journey of new product development, highlighting strategies to overcome these obstacles.
The Essence of New Product Development
New product development serves as the lifeblood of manufacturing industries, injecting freshness and modernity into the market. In the realm of plastic parts development, NPD holds the key to delivering innovative solutions that align with evolving consumer demands and technological advancements. Whether it’s creating lightweight and durable automotive components, intricate medical device parts, or consumer electronics enclosures, the process of NPD paves the way for transformation.
Challenges in New Product Development
Complex Design Requirements
The intricate geometry of plastic parts often demands meticulous design and engineering. Balancing aesthetics, functionality, manufacturability, and material selection can be a complex puzzle to solve.
Material Selection and Compatibility
Choosing the right plastic material for a specific application is crucial. The diverse range of plastic materials available, each with unique properties, can make selection challenging. Ensuring material compatibility with intended use, environmental factors, and regulatory requirements is essential.
Prototyping and Iteration
Prototyping plastic parts can be time-consuming and costly. Iterating designs and producing multiple prototypes to fine-tune the final product can significantly impact project timelines and costs.
Manufacturability and Production Scaling
Transitioning from prototyping to mass production requires careful consideration of manufacturing processes. Ensuring that the chosen manufacturing method is efficient, cost-effective, and able to maintain consistent quality at scale is a substantial challenge.
Tooling and Mold Design
Designing molds that accommodate the complex geometry of plastic parts while ensuring uniform cooling, minimal defects, and ease of ejection is a critical challenge. Tooling costs can also be substantial, impacting project budgets.
Quality Control and Testing
Ensuring the quality of plastic parts throughout the production process is paramount. Implementing rigorous quality control measures, such as dimensional accuracy testing and material strength assessments, requires careful planning.
Regulatory Compliance
Many plastic parts, especially those used in medical and automotive applications, need to meet stringent regulatory standards. Ensuring compliance with safety and quality regulations can be a daunting task.
Supply Chain and Vendor Management
Coordinating with suppliers for materials, tooling, and manufacturing processes demands efficient communication and management to avoid delays and quality issues.
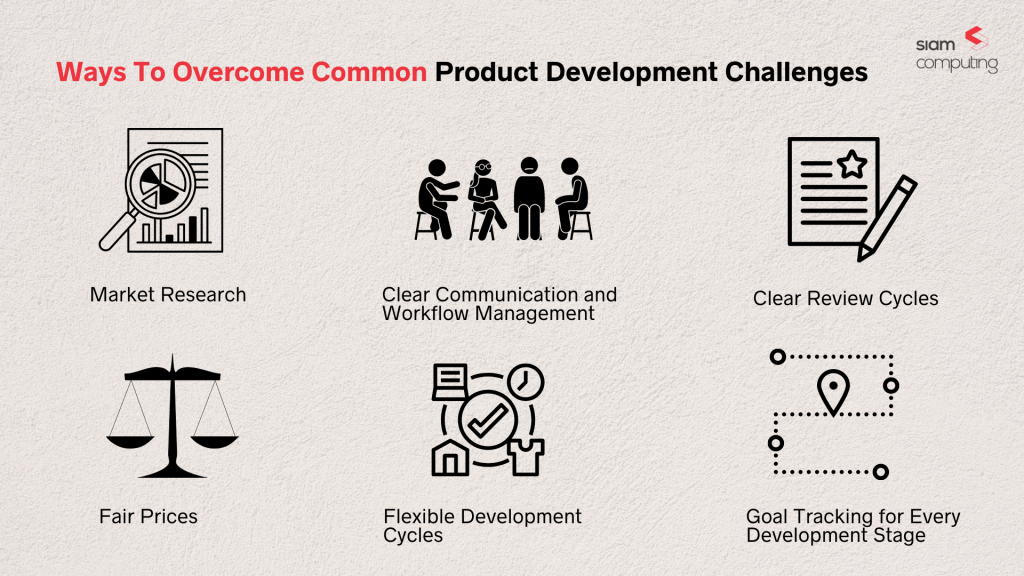
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges in New Product Development

Cross-Disciplinary Collaboration
Establishing cross-functional teams comprising designers, engineers, material experts, and manufacturing specialists fosters holistic problem-solving and ideation.
Rapid Prototyping and 3D Printing
Embracing rapid prototyping techniques and 3D printing allows for faster iterations, reduced costs, and the ability to test designs before committing to full-scale production.
Material Characterization
Thoroughly understanding the properties of different plastic materials through material testing and characterization helps in selecting the most suitable material for the application.
Simulation and Digital Twinning
Utilizing simulation software and digital twinning allows for virtual testing of designs and manufacturing processes, enabling optimizations without the need for physical prototypes.
Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
Incorporating DFM principles during the design phase ensures that the chosen design can be easily and efficiently manufactured.
Supplier Collaboration
Developing strong partnerships with suppliers and involving them in the design and development process enhances communication and helps address supply chain challenges.
Quality Assurance Plans
Implementing robust quality assurance plans, including testing and inspection protocols, ensures that the final product meets desired quality standards.
Regulatory Expertise
Collaborating with regulatory experts and consultants helps navigate the complexities of compliance and ensures that products meet industry-specific standards.
Applications of New Product Development
New Product Development (NPD) is instrumental in shaping the landscape of plastic parts manufacturing. Plastic parts are widely used across various industries due to their versatility, cost-effectiveness, and customization potential. Here are some key applications of NPD from the perspective of plastic parts development –
Automotive Industry
- Interior Components: NPD leads to the creation of innovative plastic interior components like dashboards, door panels, and center consoles that enhance aesthetics and functionality.
- Exterior Parts: Plastic parts such as bumpers, grilles, and body panels benefit from NPD to achieve lightweight and improved aerodynamics.
- Electrical and Electronics: The automotive sector utilizes NPD to develop plastic parts for wiring harnesses, connectors, and sensors.
Consumer Electronics
- Housings and Enclosures: NPD drives the creation of plastic housings and enclosures for devices like smartphones, laptops, and audio equipment.
- Connectors and Ports: Plastic connectors, USB ports, and charging ports are developed through NPD to ensure seamless device connectivity.
Medical Devices
- Diagnostic Tools: NPD contributes to the manufacturing of plastic parts used in medical diagnostic equipment such as ultrasound machines and imaging devices.
- Disposable Instruments: Plastic parts development involves creating single-use medical instruments like syringes, IV connectors, and surgical tools.
Packaging Industry
- Packaging Solutions: NPD is crucial for developing innovative plastic packaging solutions that ensure product safety, shelf life, and consumer convenience.
- Sustainable Packaging: Sustainable packaging materials and designs are achieved through NPD to address environmental concerns.
Industrial Equipment
- Conveyor Systems: NPD leads to the creation of plastic components for conveyor systems used in manufacturing and logistics.
- Safety Components: Plastic guards, covers, and safety panels for machinery are developed through NPD to enhance workplace safety.
Appliances and Household Products
- Appliance Parts: NPD drives the design and manufacture of plastic parts in appliances such as washing machines, refrigerators, and ovens.
- Home Improvement: Plastic parts for faucets, handles, and fixtures are developed through NPD to meet functional and aesthetic requirements.
Environmental Solutions
- Recycling Equipment: NPD is used to create plastic parts for recycling and waste management equipment, contributing to sustainable practices.
Electrical and Lighting
The applications of NPD in plastic parts development span numerous industries, reflecting the versatility and adaptability of plastic materials. By leveraging NPD, manufacturers can create innovative solutions that drive progress, improve efficiency, and meet the evolving demands of modern society.
Pros and Cons of New Product Development
New Product Development (NPD) is a crucial process in the realm of plastic parts manufacturing, enabling innovation, growth, and competitive edge. However, like any complex undertaking, NPD comes with its share of advantages and disadvantages. Let’s explore the pros and cons of New Product Development from the perspective of plastic parts.
Pros of New Product Development for Plastic Parts
- Innovation and Differentiation: NPD allows manufacturers to introduce innovative plastic parts with unique features, materials, and designs, setting them apart from competitors.
- Market Relevance: Keeping up with changing customer demands and market trends is easier through NPD, ensuring that plastic parts remain relevant and in demand.
- Customization and Tailoring: NPD enables the creation of customized plastic parts that cater to specific requirements of industries and applications.
- Performance Enhancement: Improved materials, designs, and manufacturing techniques achieved through NPD can lead to plastic parts with enhanced performance characteristics.
- Cost Efficiency: Well-executed NPD can lead to optimized designs that reduce material waste and production costs, ultimately benefiting the bottom line.
- Increased Revenue Streams: Successfully introducing new plastic parts expands the product portfolio and opens up opportunities for additional revenue streams.
- Improved Manufacturing Processes: NPD often involves exploring new production methods, leading to improved efficiency, reduced cycle times, and enhanced quality control.
- Collaboration and Cross-Functionality: NPD encourages collaboration among design, engineering, and manufacturing teams, fostering a holistic approach to problem-solving.
- Enhanced Brand Image: The ability to consistently deliver innovative plastic parts can bolster the brand’s image and reputation for cutting-edge solutions.
Cons of New Product Development for Plastic Parts
- High Development Costs: The research, design, prototyping, and testing phases of NPD can result in substantial upfront costs.
- Time-Consuming Process: NPD requires time for design iterations, prototyping, testing, and refinement before a final product can be launched.
- Market Uncertainty: There’s always a degree of uncertainty in how the market will receive a new plastic part, potentially leading to unanticipated challenges.
- Resource Allocation: NPD can strain resources, diverting attention and personnel away from existing product lines and operations.
- Risk of Failure: Despite meticulous planning, there’s always a risk that a new plastic part may not meet performance expectations, regulatory requirements, or customer needs.
- Competitive Pressure: The market may respond with competitive products that match or outdo the innovations introduced through NPD.
- Intellectual Property Concerns: NPD can lead to intellectual property challenges, with the risk of designs being copied or patented technologies being infringed upon.
- Logistical Complexities: Incorporating new plastic parts into the supply chain and ensuring consistent quality during mass production can present logistical challenges.
- Regulatory Hurdles: If the new plastic part is intended for specific industries like medical or automotive, navigating regulatory compliance can be intricate.
Conclusion of New Product Development
New Product Development (NPD) is a multifaceted process that holds the power to transform the landscape of plastic product manufacturing. Through the lens of plastic products, NPD emerges as a dynamic and indispensable approach that shapes industries, drives innovation, and meets evolving consumer demands. As we reflect on the journey of NPD from a plastic products perspective, several key takeaways come to light:
Innovation Catalyst: New Product Development serves as a catalyst for innovation within the realm of plastic products. It empowers manufacturers to break free from conventional boundaries, exploring novel materials, designs, and functionalities. This spirit of innovation allows for the creation of plastic products that align seamlessly with emerging trends, technological advancements, and consumer preferences.
Addressing Diverse Needs: Plastic products cater to a vast array of industries, each with its distinct requirements and challenges. New Product Development serves as a bridge that connects these diverse needs with creative solutions. From automotive to healthcare, from electronics to packaging, NPD empowers manufacturers to develop plastic products that solve real-world problems and enhance quality of life.
Strategic Advantage: Embracing New Product Development confers a strategic advantage upon manufacturers in the competitive market landscape. The ability to introduce cutting-edge plastic products not only positions a brand as a leader in innovation but also opens doors to new markets and revenue streams. By continuously pushing the boundaries of what plastic products can achieve, companies set themselves apart and secure a lasting competitive edge.
Holistic Approach: The New Product Development process for plastic products demands a holistic approach that spans ideation, design, prototyping, testing, and production. It encourages collaboration among multidisciplinary teams, fostering an environment where designers, engineers, and manufacturing experts work together seamlessly. This collaborative synergy ensures that the end product meets not only aesthetic and functional requirements but also manufacturing feasibility and efficiency.
Balancing Challenges and Rewards: The journey of New Product Development for plastic products is not without its challenges. High development costs, time-consuming iterations, market uncertainties, and regulatory complexities can pose obstacles. However, these challenges are balanced by the rewards of innovation, market relevance, and differentiation. With a clear understanding of both the pros and cons, manufacturers can navigate these challenges effectively and make informed decisions.
Sustainable Progress: In an era marked by environmental consciousness, New Product Development for plastic products also embraces sustainability as a guiding principle. The development of eco-friendly materials, recyclable designs, and energy-efficient production methods underscores the commitment to responsible innovation. NPD allows manufacturers to contribute positively to the environment while meeting consumer expectations for sustainability.
In essence, New Product Development from the perspective of plastic products signifies an ongoing commitment to progress and evolution. It is a process that empowers manufacturers to transcend boundaries, transcend limitations, and pave the way for a future where plastic products continue to shape industries, enhance experiences, and make a meaningful impact on the world. Through strategic vision, innovative thinking, and an unwavering dedication to excellence, NPD transforms the potential of plastic products into tangible realities that shape our present and inspire our future.
FAQ’s
What is a New Product Development Process?
The New Product Development (NPD) process is a structured approach that organizations use to bring new products or services from concept to market. It involves a series of steps and activities aimed at identifying market opportunities, conceptualizing ideas, designing, developing, testing, and ultimately launching the product. The NPD process ensures that the new product meets customer needs, aligns with business goals, and is delivered efficiently.
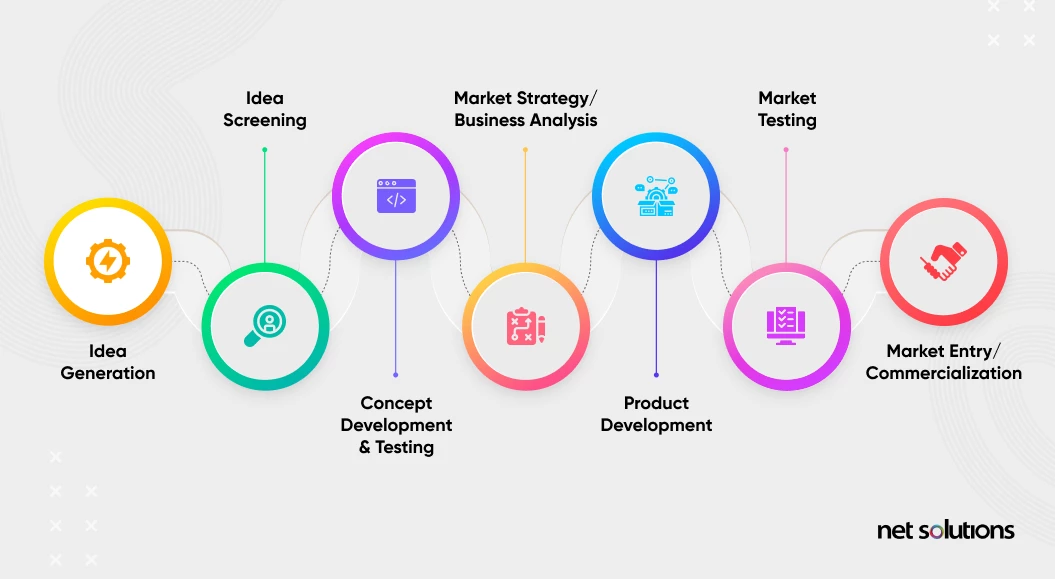
The key stages of the New Product Development process typically include idea generation, idea screening, concept development and testing, business analysis, product development, market testing, and commercialization. Throughout these stages, cross-functional teams collaborate to bring the product to life while considering factors such as market trends, competition, technological feasibility, and consumer feedback. The New Product Development process helps minimize risks, optimize resources, and increase the chances of success for new products in the market.
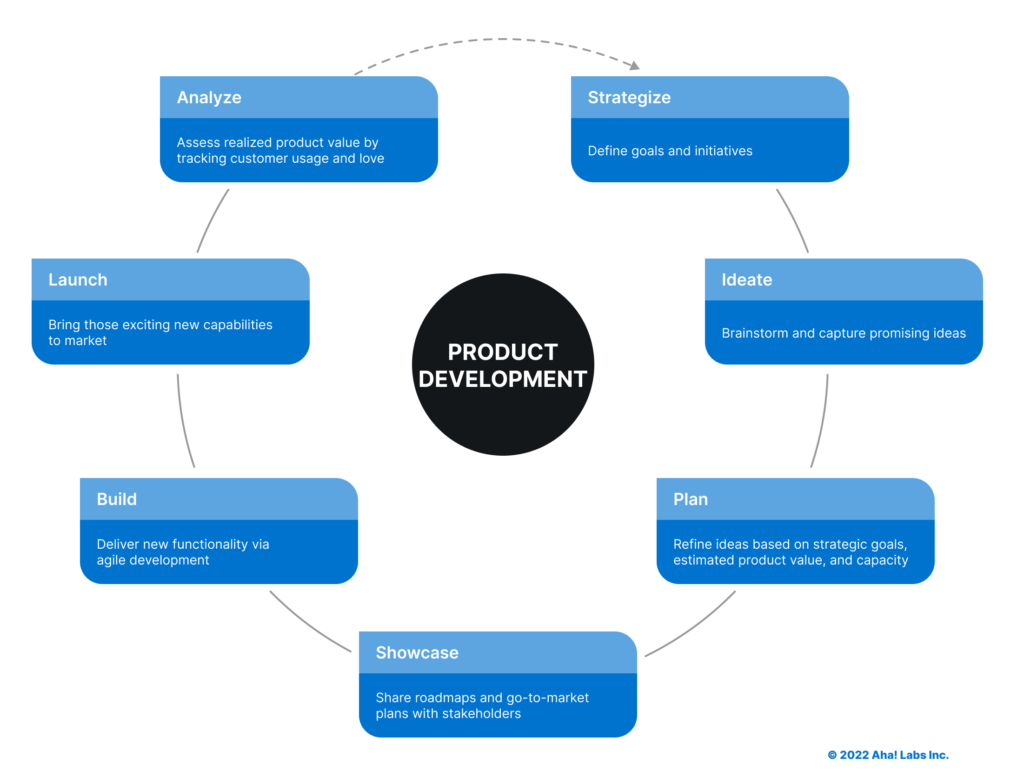
Explain about New Product Development Stages.
New Product Development (NPD) stages represent the sequential steps a product goes through from conception to launch. These stages ensure a structured approach to creating successful products that meet market demands and organizational objectives. Here’s a brief overview of the key New Product Development stages –
Idea Generation: This stage involves brainstorming and collecting ideas for potential new products. Ideas can come from customers, employees, research, or other sources.
Idea Screening: In this stage, the collected ideas are evaluated to filter out those that are unfeasible, too costly, or not aligned with the company’s strategy.
Concept Development and Testing: Selected ideas are elaborated into concepts. Concepts include preliminary descriptions, features, and benefits. These concepts are then tested with target customers to gather feedback and refine them.
Business Analysis: A thorough analysis is conducted to assess the viability and profitability of the selected concept. This includes estimating costs, potential sales, market share, and return on investment.
Product Development: Once the concept is approved, the product development stage begins. Engineers and designers create prototypes or develop the actual product, considering factors like design, functionality, and manufacturing processes.
Market Testing: A small-scale launch or pilot is conducted in a specific market to evaluate real-world customer reactions, gather feedback, and identify any potential issues before a full launch.
Commercialization: If the market testing is successful, the product moves to the commercialization stage. This involves full-scale production, marketing campaigns, distribution, and the official launch in the target markets.
Post-Launch Evaluation: After the product is launched, its performance is continuously monitored. Sales, customer feedback, and other metrics are analyzed to ensure the product is meeting its goals and making necessary adjustments.
These stages provide a systematic framework for bringing a new product to market while considering aspects like market demand, feasibility, profitability, and customer satisfaction. Effective management of each stage contributes to the successful introduction of innovative products that resonate with customers and drive business growth.