The automotive industry is constantly evolving, with engineers and manufacturers relentlessly pursuing innovation to create vehicles that are safer, more fuel-efficient, and environmentally friendly. In this quest for excellence, materials play a pivotal role, and one polymer that has made a significant impact in automotive engineering is Polypropylene (PP). This versatile plastic has found its way into various components and applications within vehicles, where its unique combination of strength, durability, and efficiency has reshaped the automotive landscape.
The Rise of Polypropylene (PP) in the Auto Industry
Polypropylene, a thermoplastic polymer, was first synthesized in the 1950s, and its popularity in the automotive industry has grown steadily since then. PP has several attributes that make it an ideal choice for automotive applications –
1. Lightweight yet Strong: PP is lightweight, making it an attractive choice for components where weight reduction is crucial for fuel efficiency. Despite its low density, PP exhibits remarkable strength, making it suitable for both structural and non-structural parts.
2. Chemical Resistance: PP is highly resistant to chemicals, including automotive fluids like oils and fuels. This property ensures the longevity and reliability of PP components in the harsh automotive environment.
3. Impact Resistance: PP’s ability to absorb impact energy makes it valuable for parts that require protection against collisions, such as bumpers.
4. Recyclability: The automotive industry is increasingly focused on sustainability, and PP’s recyclability aligns with this goal. Recycled PP can be used to create new automotive components, reducing the industry’s environmental footprint.
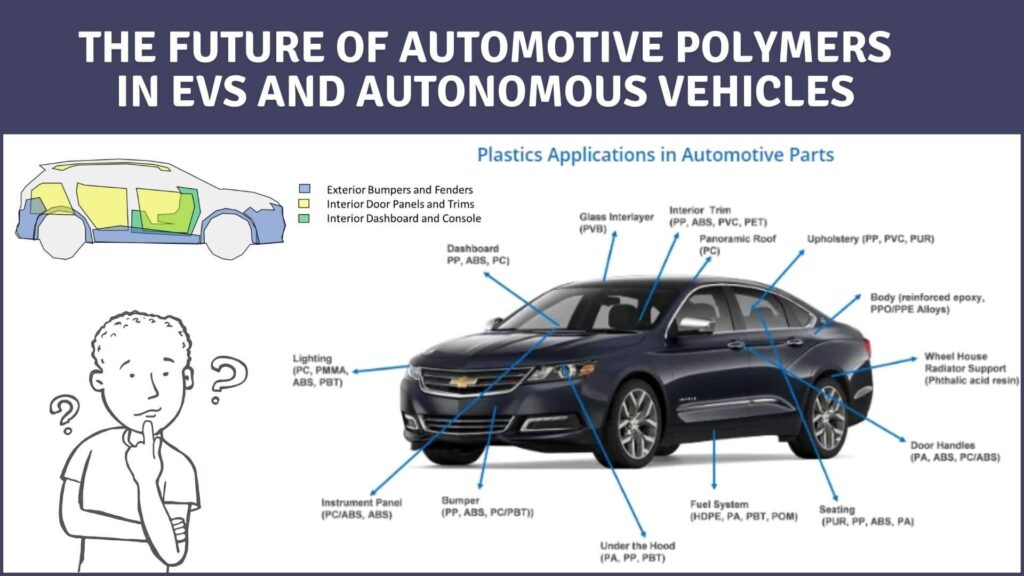
Key Applications of Polypropylene (PP) in Automotive Engineering

- Bumpers
- PP is a preferred material for manufacturing bumper systems due to its excellent impact resistance. Bumpers made of PP can absorb energy during minor collisions, reducing the risk of damage to the vehicle’s structure.
2. Interior Components
- PP is extensively used in the production of interior components such as door panels, dashboard covers, and trim parts. Its low cost, durability, and ease of processing make it an ideal choice for these applications.
3. Underbody Shields
- PP is used in the fabrication of underbody shields, which protect the vehicle’s undercarriage from debris and impacts. These shields help improve aerodynamics and fuel efficiency.
4. Interior Fabrics
- PP-based materials are used in automotive upholstery, contributing to the comfort and aesthetics of vehicle interiors. PP fabrics are durable, stain-resistant, and easy to clean.
5. Fuel Tanks
- PP is used in the manufacturing of fuel tanks, where its chemical resistance ensures the safe storage of gasoline and diesel fuels. The lightweight nature of PP tanks also contributes to fuel efficiency.
6. Air Intake Manifolds
- PP is employed in the production of air intake manifolds, where its combination of strength and heat resistance is critical. PP manifolds are durable and can withstand the high temperatures of engine operation.
7. Battery Cases
- In electric vehicles (EVs), battery cases made from PP offer excellent insulation properties and chemical resistance. These cases protect the vehicle’s battery pack, ensuring safety and longevity.
8. Exterior Trims
- PP is used for various exterior trims, such as fenders, side mirrors, and grilles. These components require a material that can withstand exposure to the elements, and PP’s durability makes it an ideal choice.
9. Noise, Vibration, and Harshness (NVH) Components
- PP is employed in NVH components to reduce noise and vibrations in the vehicle’s cabin. These components enhance the overall comfort and driving experience.

The Environmental Aspect: PP and Sustainability
Sustainability is a core concern in the automotive industry, and PP aligns with this focus in several ways –
1. Lightweighting: PP’s low density contributes to the vehicle’s lightweight, which is essential for improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. Lighter vehicles require less fuel to operate and produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Recyclability: PP is recyclable, and automotive manufacturers are increasingly incorporating recycled PP into their production processes. This reduces the demand for virgin PP and minimizes waste.
3. Fuel Efficiency: As a lightweight material, PP contributes to better fuel efficiency, particularly in internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. Improved fuel efficiency means lower carbon emissions.
4. Electric Vehicles (EVs): In the EV market, PP’s properties are particularly valuable for battery cases, helping to ensure the safety and reliability of electric powertrains.
Challenges and Innovations
While PP offers numerous advantages in automotive engineering, it’s not without its challenges. High-temperature applications, such as engine components, demand materials with superior heat resistance. To address this, researchers and manufacturers are developing advanced PP formulations with enhanced thermal stability.
Another challenge lies in improving the recyclability of PP materials used in vehicles. Innovations in recycling technologies are crucial to efficiently recover and reuse PP from end-of-life vehicles, reducing the environmental impact of automotive waste.
The Future of PP in Automotive Engineering
Polypropylene’s journey in the automotive industry is far from over. As the industry continues to evolve, driven by electrification, autonomous driving, and sustainability goals, PP will play an increasingly significant role. Future innovations may lead to even more advanced PP formulations tailored to the unique requirements of next-generation vehicles.
In conclusion, Polypropylene (PP) has emerged as a crucial material in automotive engineering, offering a blend of strength, efficiency, and sustainability. Its diverse applications, from bumpers to interior components and fuel tanks, demonstrate its versatility and reliability. As the automotive industry continues to adapt to changing technologies and environmental challenges, PP is set to remain a driving force behind innovation and progress in vehicle design and manufacturing.
Polypropylene (PP) Material: Properties, Processing, Characteristics & Applications
here is an overview of Polypropylene (PP) material, covering its properties, processing, characteristics, and applications in a step-wise format –
Properties of Polypropylene (PP)
- Chemical Structure: Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer composed of propylene monomers. Its chemical structure contributes to its excellent chemical resistance.
- Density: PP is a low-density material, which means it is lightweight and ideal for applications where weight reduction is essential.
- Melting Point: It has a relatively high melting point, typically around 160-170°C (320-338°F), making it suitable for various manufacturing processes.
- Chemical Resistance: PP exhibits exceptional resistance to chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents, making it ideal for applications where exposure to corrosive substances is expected.
- Impact Strength: PP possesses good impact resistance, making it suitable for components that need to withstand mechanical stresses.
- Flexibility: It is a flexible material, and its flexibility increases with the addition of copolymers, making it versatile for various applications.
Processing of Polypropylene (PP)
- Extrusion: PP can be extruded into various forms, such as sheets, films, and pipes, using extrusion processes.
- Injection Molding: Injection molding is a common method for manufacturing complex shapes and components using PP. It is widely used in the automotive and consumer goods industries.
- Blow Molding: Blow molding is employed to create hollow products like bottles and containers from molten PP.
- Thermoforming: Thermoforming involves heating PP sheets and forming them into desired shapes using molds.
- Fiber Spinning: PP can be processed into fibers for applications like textiles, ropes, and geotextiles.
Characteristics of Polypropylene (PP)
- Lightweight: PP is lightweight, making it suitable for applications that require weight reduction, such as automotive components.
- High Heat Resistance: It can withstand relatively high temperatures without deforming, making it suitable for hot-fill applications.
- Low Moisture Absorption: PP has low moisture absorption properties, which is beneficial in applications where moisture resistance is essential.
- Excellent Chemical Resistance: Its resistance to various chemicals is a significant advantage, especially in corrosive environments.
- Recyclability: PP is recyclable, and recycled PP can be used to create new products, contributing to sustainability efforts.
Applications of Polypropylene (PP)
- Packaging: PP is widely used in packaging materials, including plastic bags, films, and containers.
- Automotive Components: PP is found in automotive bumpers, interior trim, and underbody shields due to its lightweight yet durable nature.
- Textiles: PP fibers are used in textiles, such as carpeting, upholstery, and geotextiles.
- Medical Devices: PP is used in medical devices and packaging due to its biocompatibility and chemical resistance.
- Consumer Goods: It is utilized in various consumer products, including toys, kitchenware, and household appliances.
- Industrial Applications: PP pipes, sheets, and containers serve industrial needs, such as chemical storage and transport.
- Electronics: PP is used in electrical and electronic components due to its electrical insulating properties.
- Agriculture: PP films are employed in agriculture for crop protection and greenhouse applications.
- Battery Cases: In electric vehicles (EVs), PP is used for battery cases to ensure safety and chemical resistance.

Frequently Asked Questions
What is Polypropylene (PP)?
Polypropylene (PP) is a versatile thermoplastic polymer derived from propylene monomers. It is known for its lightweight, chemical resistance, and durability.
What are the key properties of Polypropylene (PP)?
The key properties of PP include low density, high melting point, chemical resistance, impact strength, flexibility, and recyclability.
What are the common forms of Polypropylene (PP)?
PP is available in various forms, including sheets, films, fibers, and molded parts.
Is Polypropylene (PP) safe for food contact and medical applications?
Yes, PP is generally considered safe for food contact and medical applications due to its chemical resistance and biocompatibility.
How is Polypropylene (PP) recycled?
PP can be recycled through processes such as mechanical recycling, which involves melting and reusing PP materials to create new products.
What industries use Polypropylene (PP) extensively?
PP is widely used in industries such as packaging, automotive, textiles, healthcare, and agriculture.
What makes PP suitable for automotive applications?
PP’s combination of lightweight properties, chemical resistance, and impact strength makes it ideal for automotive components like bumpers and interior trim.
Does Polypropylene (PP) contribute to sustainability efforts?
Yes, PP is recyclable, and its lightweight nature helps reduce fuel consumption in vehicles, contributing to sustainability goals.
Are there any limitations to Polypropylene (PP)?
While PP has many advantages, it can have limited resistance to high temperatures and UV radiation. Special formulations can address these limitations.
Can Polypropylene (PP) be used in 3D printing?
Yes, PP can be used in 3D printing, offering design flexibility and durability in printed parts.
How is PP different from other common plastics like Polyethylene (PE) and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)?
PP differs from PE and PVC in terms of its properties, such as higher melting points and better chemical resistance. Each plastic has distinct applications based on its properties.
What are the emerging innovations related to Polypropylene (PP)?
Researchers are exploring bio-based PP materials and advanced recycling techniques to enhance sustainability and reduce environmental impact.
Is Polypropylene (PP) a sustainable choice in packaging materials?
Yes, PP is considered a sustainable choice in packaging due to its recyclability and lightweight properties, which reduce transportation-related emissions.
Can PP be used for outdoor applications?
PP can be used for outdoor applications with appropriate additives to enhance UV resistance, making it suitable for products like outdoor furniture.
How does PP contribute to reducing the environmental impact of the automotive industry?
PP’s lightweight nature reduces the overall weight of vehicles, leading to improved fuel efficiency and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.


I’d have to examine with you here. Which is not one thing I usually do! I take pleasure in reading a post that may make folks think. Additionally, thanks for permitting me to comment!
I’ve recently started a website, the information you provide on this website has helped me tremendously. Thank you for all of your time & work.
Well researched
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Hi there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this article to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
I’ve read several just right stuff here. Certainly value bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how so much attempt you set to create one of these excellent informative website.
Having gone through a similar experience myself, I found your insights particularly validating. You captured emotions I struggled to articulate, which made me feel less alone in my journey. Thank you for sharing something so personal.